Figure 2.
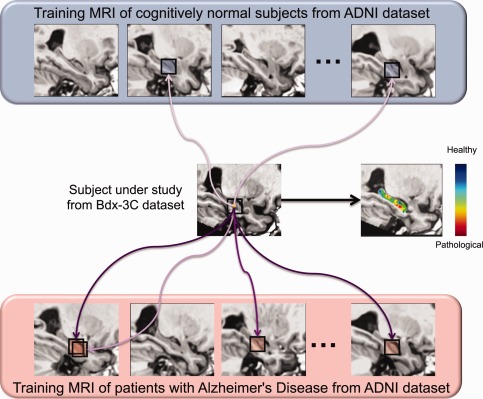
General principle of hippocampal grading by pathological pattern recognition. The figure presents the anatomical pattern recognition strategy for one voxel of subject under study by displaying only few similar anatomical patterns found in training MRI. This procedure is repeated for all the voxels of the subject under study over the hippocampus to obtain the final grading map. In this example the Bdx‐3C subject under study is a cCN subject. Purple arrows symbolize the similarity between anatomical patterns. Dark purple indicates high anatomical patterns similarity and light purple indicates low similarity. For the anatomical pattern under study in this example derived from a cCN subject, more similar anatomical patterns are found in AD population and their weights (similarities) are higher. In the grading map, when the voxel color is blue it indicates that the anatomical pattern surrounding this voxel is more similar to anatomical patterns found in the CN training subjects and thus that the local anatomy is closer to anatomies of healthy subjects (i.e. CN‐like anatomical pattern). When the voxel color is green it indicates that the anatomical pattern is equally similar to anatomical pattern found in the CN and the AD training subjects. Finally, when the voxel color is red it indicates that the local anatomy contains alterations typical of the AD population (i.e. AD‐like anatomical pattern) and thus the presence of neurodegeneration. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com.]
