Figure 1.
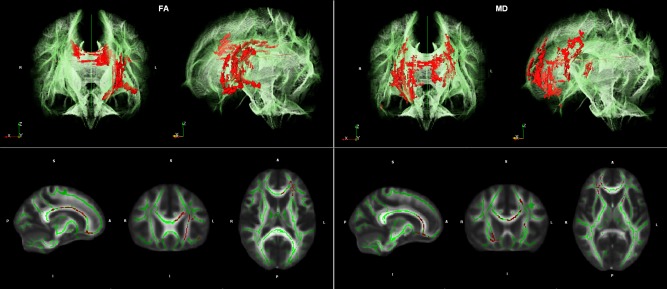
Illustration of results of the Tract‐based spatial statistic (TBSS) regression analyses. Regions with significant correlations (red) between fractional anisotropy (FA) measures and Stroop interference (left) as well as mean diffusivity (MD) measures and Stroop interference (right) are projected on cerebral white matter skeleton (green) in two different views (3D above, 2D below). TBSS results showed significant negative correlations (corrected P < 0.25) between FA values and Stroop interference in fronto‐parietal regions including the genu and body of Corpus Callosum (CC) and the left anterior corona radiata (left). Furthermore, TBSS analyses demonstrated significant positive correlations between MD values and Stroop interference in genu and body of CC, bilateral anterior corona radiata, and left anterior limb of capsula interna (right).
