Figure 3.
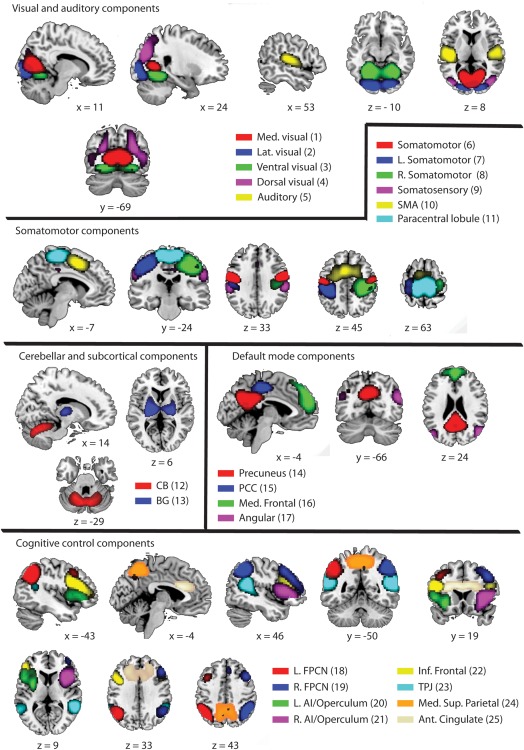
Identified independent components (ICs), grouped by location and function. The number between brackets indicates the IC number. Within the identified ICs, there were four visual components, representing the medial (IC1), lateral (IC 2), ventral (IC3), and dorsal (IC4) parts of the visual system. In addition, one auditory component (IC 5) was identified. Six different components were identified that are related to sensorimotor functions (IC 6‐11). Separate ICs were identified for the cerebellum (IC 12) and the basal ganglia (IC 13). The classical default mode network was represented in four separate components (IC 14‐17). Separate left and right fronto‐parietal components were identified (IC 18 and 19, respectively) as well as left and right anterior insula/opercular networks (IC 20 and 21, respectively). Bilateral inferior frontal (IC 22) and temporo‐parietal junction components (IC 23) were identified as well as medial superior parietal (IC 24) and anterior cingulate components (IC 25). R = right, L = left, Ant = anterior, Inf = inferior, Sup = superior, Lat = lateral, Med = medial, SMA = supplementary motor area, CB = cerebellum, BG = basal ganglia, PCC = Posterior Cingulate Cortex, FPCN = fronto‐parietal control network, AI = anterior insula, TPJ = temporo‐parietal junction.
