Figure 3.
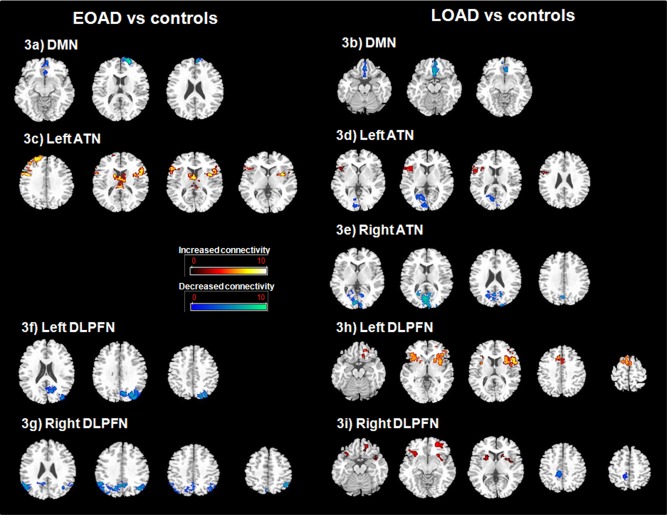
Differences in resting state functional connectivity (FC) maps between EOAD and young controls (a; c; f; g), LOAD and age‐matched controls (b; d; e; h; i) (P < 0.005, k > 10; FWE corrected at the cluster level, P < 0.05) (radiological convention: left is right). a: Decreased FC of DMN in EOAD relative to matched controls. EOAD show decreased FC of the DMN connectivity map derived from the PCC as seed region within the superior, middle and medial frontal gyri (Brodmann area‐BA 10, BA 11). b: Decreased FC of DMN in LOAD relative to matched controls. LOAD show decreased FC of the DMN connectivity map derived from the PCC as seed region within the medial frontal gyri (BA 10, BA 11, BA 25). c: Increased FC of the left ATN in EOAD relative to matched controls. EOAD show bilateral increased FC of the ATN connectivity map derived from the left perirhinal cortex as seed region within the inferior frontal gyrus (BA44, BA45), the middle and superior frontal gyri (BA 9, BA 10, BA 46), the thalamus, caudate nucleus and insula (BA 13). d: Increased (hot) and decreased (blue) FC of the left ATN in LOAD relative to matched controls. LOAD show increased FC of the ATN connectivity maps derived from the left perirhinal cortex as seed region within the right inferior frontal gyrus (BA 9, BA 44, BA 45) and the right insula (BA 13) while reduced connectivity was observed in the right lingual gyrus, the right and left calcarine sulcus and posterior cingulate (BA 30, BA 31). e: Decreased FC of the right ATN in LOAD relative to matched controls. LOAD show decreased FC of the ATN connectivity maps derived from the right perirhinal cortex as seed region within bilateral occipital regions (cuneus, BA 18) and right precuneus‐posterior cingulate (BA 31). f: Decreased FC of the left DLPFN in EOAD relative to matched controls. EOAD show decreased FC of the DLPFN connectivity maps derived from the left dorso‐lateral prefrontal cortex as seed region within the left middle occipital gyrus, cuneus, precuneus (BA 7, BA 19) and the left inferior parietal lobule. g: Decreased FC of the right DLPFN in EOAD relative to matched controls. EOAD show decreased FC of the DLPFN connectivity maps derived from the right dorso‐lateral prefrontal cortex as seed region within bilateral cuneus, precuneus (BA7, BA 19) and inferior parietal lobules. h: Increased FC of the left DLPFN in LOAD relative to matched controls. LOAD show increased FC of the DLPFN connectivity maps derived from the left dorso‐lateral prefrontal cortex as seed region within the inferior frontal gyrus (BA 11‐BA 44), precentral (BA 6) and middle cingulate (BA 32) gyri, insula (BA 13) and striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen). i: Increased (hot) and decreased (blue) FC of the right DLPFN in LOAD relative to matched controls. LOAD show increased FC of the DLPFN connectivity maps derived from the right dorso‐lateral prefrontal cortex as seed region within the bilateral inferior and middle frontal gyri (BA 11, BA 47), insula and putamen while decreased FC in the precuneus/cingulate gyrus (BA 7) is observed.
