Figure 5.
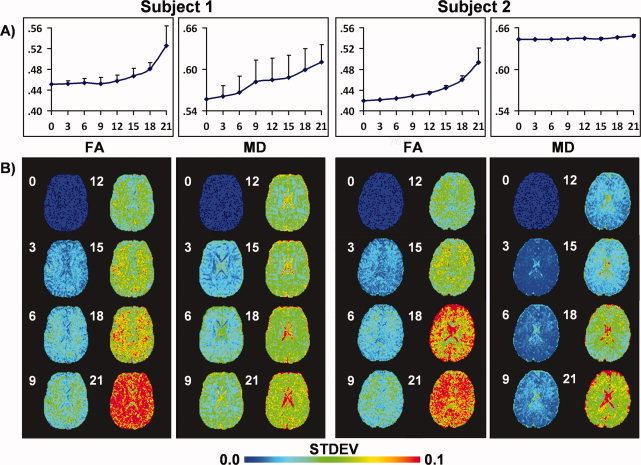
Effects of randomly removing diffusion weighted (DW) images on both fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) across two different subjects (please see Supp. Info., Fig. 3 for third subject). DW images were randomly selected and removed in multiples of 3 (e.g., three DW images, six DW images, etc.) before the calculation of the diffusion tensor, with each step being repeated 30 times. A presents results of a histogram analysis for all white matter voxels. The circles correspond to the mean scalar value and the error bars represent one standard deviation derived from all 30 iterations. The number of gradients removed is indicated along the x‐axis. For both subjects, a positive bias existed in the FA data associated with increasing the number of gradients removed. A positive bias was also present for two of three subjects for MD (see Supp. Info., Fig. 4), with Subject 2 exhibiting a relatively stable mean. B presents the variation in scalar values on a voxelwise basis following the random removal of gradients. For all subjects, voxelwise precision in the calculation of DTI scalar metrics decreased as a function of randomly removing DW images.
