Figure 2.
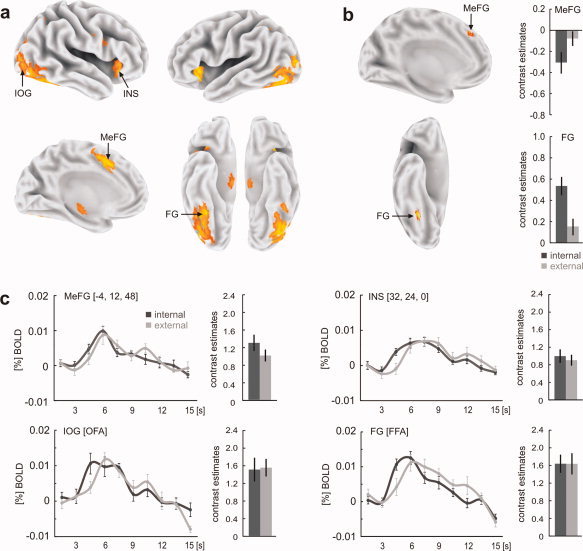
(a) Comparing functional activations during the face‐string sequence with those of the scrambled sequence irrespective of encoding style revealed a distributed activation pattern including activations in the inferior occipital gyrus (IOG), fusiform gyrus (FG), anterior insular cortex (INS), and medial frontal gyrus (MeFG). (b) Internal encoders showed higher activation in the right FG whereas external encoders showed higher activation in MeFG. (c) Individual face responsive regions in extrastriate brain regions were determined using functional face localizer scans. Across all subjects, we found right hemispheric regions in the inferior occipital gyrus and the fusiform gyrus that most probably represent the occipital face area (OFA) and the fusiform face area (FFA), respectively. Although both areas revealed no significant differences in activation between internal and external encoders, the time course of the BOLD response in both areas revealed an earlier latency peak in the group of internal encoders. Functional contrasts were rendered on the human Colin atlas implemented in the CARET software [Van Essen et al., 2001]. Coordinates refer to the MNI space; error bars indicate SEM. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]
