Figure 3.
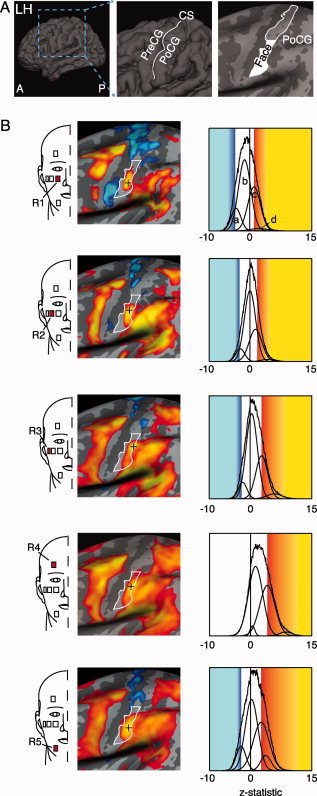
Localization of brush activation in left S1. (A) The first image is a reconstruction of the left hemisphere (LH) of an average brain (n = 12 subjects) subsequent to co‐registration using cortical surface‐based alignment via Freesurfer. A = anterior and P = posterior. The middle image is a magnified view of the central sulcus (CS) with labels for precentral gyrus (PreCG) and post‐central gyrus (PoCG). The image on the right is a brain that has been “inflated” to better visualize gray matter within the sulci, such that gyri are colored light gray and sulci are dark gray. This image highlights the approximate face representation in S1 as the inferior half of the PoCG. B) Group brush activation maps across stimulation sites. Red squares identified by number indicate the location of each stimulus. Significant positive (red to yellow) and negative activation levels (dark blue to light blue) based on stimulus‐based GLM analyses are displayed. Black crosses indicate the activation maxima. For visual presentation purposes, the group statistical maps were spatially smoothed using a 3.5 mm FWHM kernel. The z‐statistic distribution for each activation map is shown to the right. The y‐axis represents the relative population distribution. Z‐statistic thresholds were determined using GMM (Gaussian mixture modeling), which identified distinct distributions (modeled as gaussian curves) for positive and negative activations. The entire set of gaussian distributions for activation for each stimulus site is displayed in each graph. In region 1, four distributions were detected using GMM, with distributions for negative activation (a), noise (b), and positive activation (c, d). The threshold for significant activation was identified as the mode of the dominant positive and negative distributions. If the mode of the positive or negative distribution was below the relative contribution of the null distribution, the activation distribution was considered not significant. For further details on GMM, refer to [Becerra et al., 2006; Moulton et al., 2007; Pendse et al., 2006].
