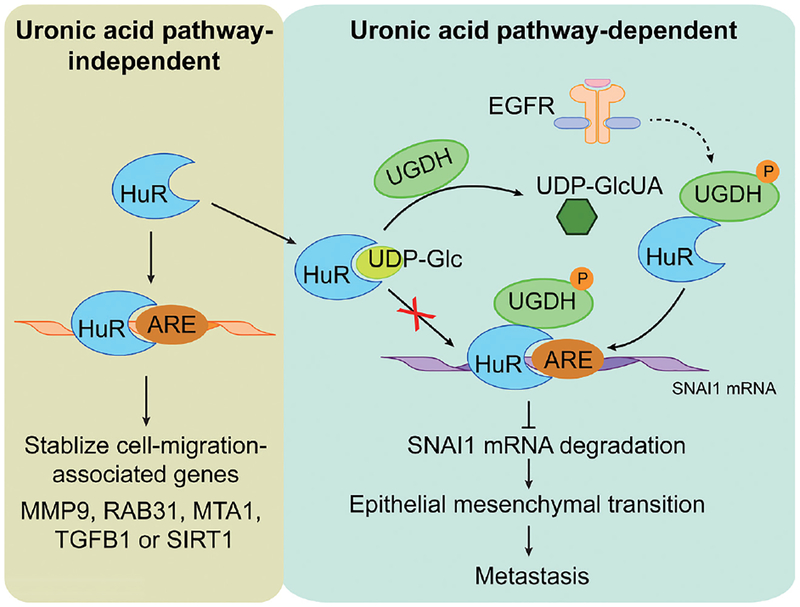
Figure 2.
Schematic model of the mechanism of HuR-regulated tumor cell migration. Left panel, HuR stabilizes the mRNAs of cell-migration-associated genes via a uronic acid pathway-independent mechanism. Right panel, HuR reduces the SNAI1 mRNA degradation via a uronic acid pathway-dependent mechanism. Upon EGFR activation, phosphorylated UGDH converts UDP-Glc into UDP-GlcUA and release HuR to bind ARE and stabilize SNAI1 mRNA. Increased SNAI1 mRNA expression enhances the epithelial mesenchymal transition and promotes cancer metastasis. UGDH, UDP-glucose dehydrogenase; GlcUA, glucuronic acid; ARE, adenylate uridylate rich element; UDP, uridine diphosphate.