Figure 7.
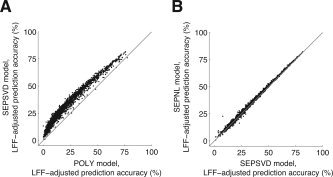
Time‐event separability reduces overfitting and increases prediction accuracy. In these graphs we compare the FIR model to the time‐event separable model (Table I). Each point in a graph represents prediction accuracy for a single voxel. (A) POLY vs. SEPSVD. The x‐ and y‐axes indicate the LFF‐adjusted prediction accuracy under the POLY and SEPSVD models, respectively. The graph depicts voxels with a minimum SNR of 10 under either data model (n = 1,884). There was a large increase in accuracy under the SEPSVD model compared to the POLY model (median increase 9.9%; P < 0.001). This indicates that voxel responses were largely time‐event separable, and that time‐event separability improved the accuracy of HDR estimates. (B) SEPSVD vs. SEPNL. The x‐ and y‐axes indicate the LFF‐adjusted prediction accuracy under the SEPSVD and SEPNL models, respectively. The graph depicts voxels with a minimum SNR of 10 under the POLY model (n = 1,730). There was a tiny increase in accuracy under the SEPNL model compared to the SEPSVD model (median increase 0.5%; P < 0.001). This indicates that the singular value decomposition fitting method compared favorably against the iterative fitting method in this data set.
