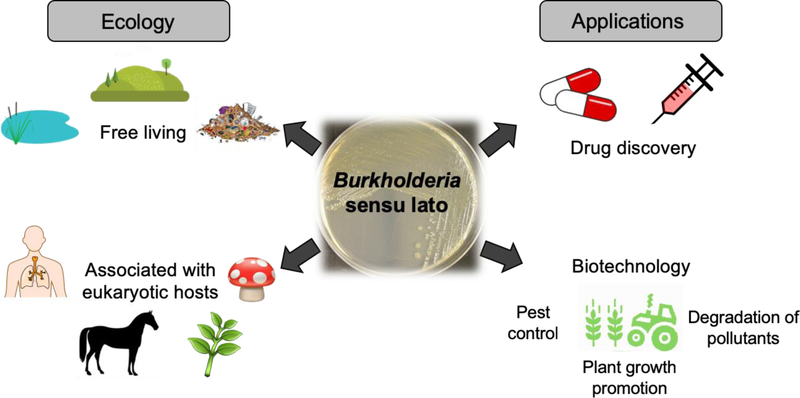
Figure 1.
Overview of Burkholderia sensu lato, its ecological roles and potential applications. Members of Burkholderia sensu lato occupy diverse ecological niches ranging from pristine soil and aquatic environments to contaminated landfill, and they can be free-living or associated with a wide set of eukaryotic hosts, from fungi to humans. Host associations can be harmful (e.g. human and animal pathogens that include biological warfare agents) or beneficial (e.g. endosymbionts that promote plant growth). Ecological niche diversity translates into diverse natural products that mediate host interactions, that are beneficial for adaptation and survival, and that may be harnessed for biotechnological applications and drug discovery.