Figure 6.
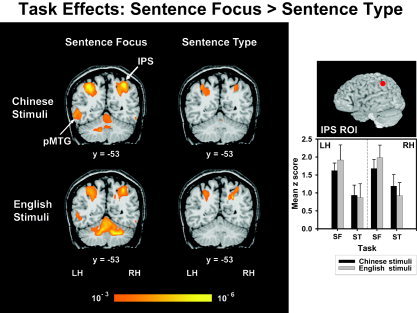
Random effects fMRI activation maps obtained from within‐stimulus (Chinese, top; English, bottom) comparisons of discrimination judgments of sentence focus (left) and sentence type (right) relative to the control condition (passive listening). Coronal sections in a standard stereotactic space are superimposed onto a representative brain anatomy (y = −53). IPS, intraparietal sulcus; pMTG, posterior superior temporal gyrus. Increased activity is observed in the left pMTG and bilateral IPS in the sentence focus task relative to sentence type for both language stimuli. A comparison of mean z scores between tasks (SF, ST) per hemispheres (LH, RH) and language stimuli (Chinese, English) is shown in a bar chart for the IPS ROI. See also Figure 3 for a bar chart comparing mean z scores between tasks in the pMTG per hemisphere (LH, RH) and language stimuli (Chinese, English). See also Figure 3 caption.
