Figure 1.
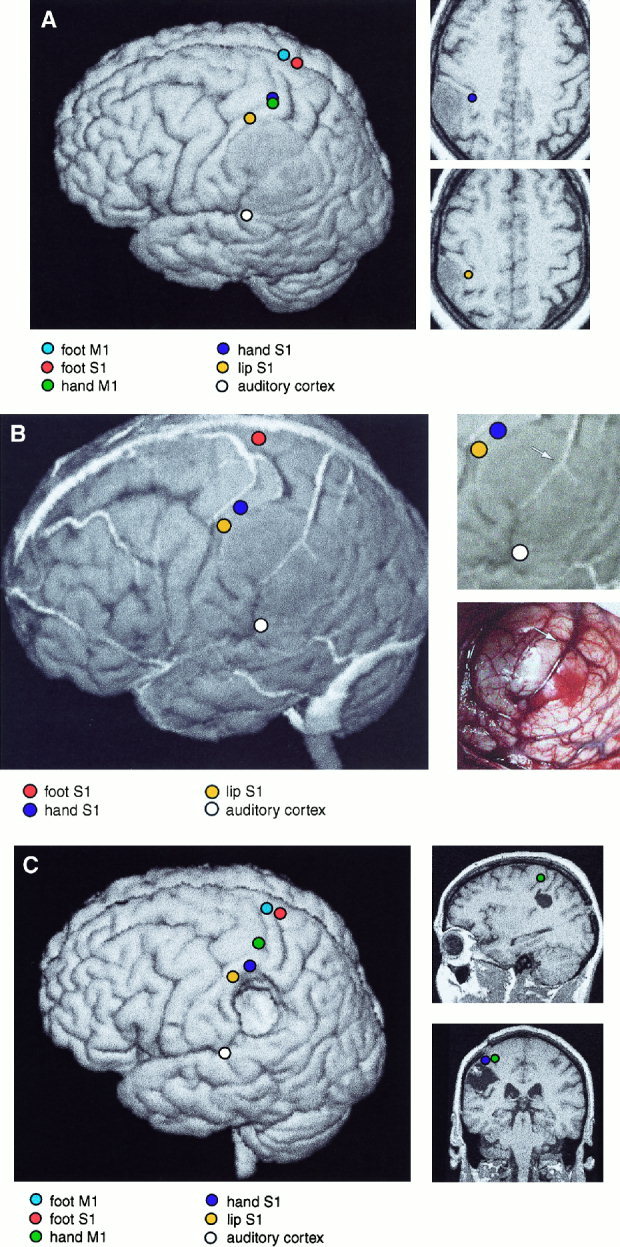
A:Left: 3‐D surface rendering of the brain of Patient 9. The left parietal GII oligoastrocytoma is readily identifiable. The equivalent current sources of responses to MN‐SEFs, TN‐SEFs, LIP‐SEFs and AEFs, and MEG‐EMG coherences for right wrist and ankle extensions are displayed on the surface. Right: Sources of SEFs to median nerve and lip stimulation, displayed on two horizontal MRI sections. Note the distortion of functional cortical anatomy by the slowly growing tumor. B.Left: 3‐D surface rendering of the brain of Patient 9, including cortical veins and sources of SEFs and AEFs. Right, above: Enlarged section of 3‐D MRI surface rendering. Right, below: Corresponding brain surface during surgery. The veins are readily identifiable and allow both the localization of the somatosensory cortex (left) and the tumor area (right, below) (vein bifurcation over the tumor is marked with an arrow). C. Left: Postoperative surface rendering of Patient 9. Sources of MEG‐EMG coherences for right wrist and ankle extensions, and MN‐SEFs, TN‐SEFs, LIP‐SEFs and AEFs, are displayed on the surface. Right: Sagittal and coronal sections of the postoperative MRIs, with sources of median nerve SEFs and hand MEG‐EMG coherence.
