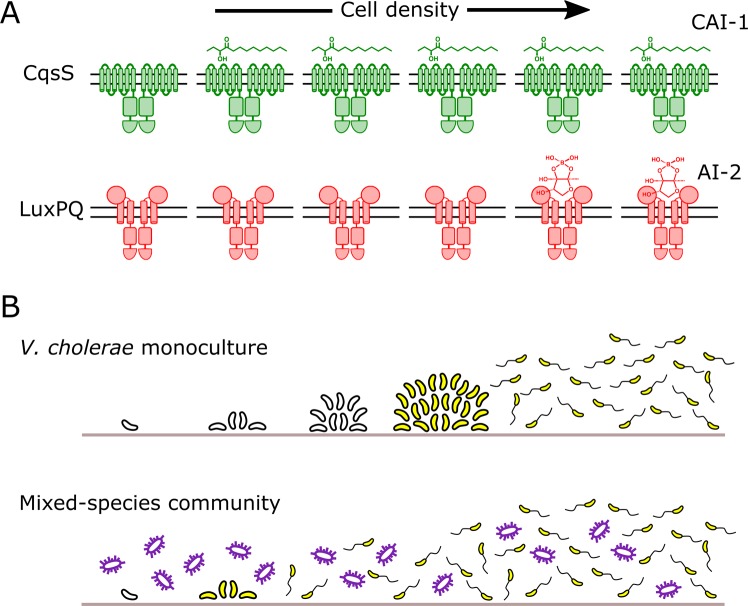
Fig 8. Asymmetric autoinducer thresholds drive distinct intragenus and interspecies QS responses.
(A) CAI-1 produced by V. cholerae engages its cognate CqsS receptor at very low cell densities. In contrast, AI-2 does not accumulate to sufficient levels to engage its cognate LuxPQ receptor until much higher cell densities. (B) The consequence of asymmetric receptor occupancy coupled with the QS system functioning as a coincidence detector is that AI-2 sets the pace at which QS occurs. In V. cholerae monoculture (top), the absence of AI-2 at LCD is required for biofilm formation. Thus, exogenous AI-2, such as that provided in mixed-species communities by bacteria that possess LuxS, presumably represses V. cholerae biofilm development and/or promotes dispersal (bottom). AI-2, autoinducer-2; CAI-1, cholerae autoinducer-1; LCD, low cell density; QS, quorum sensing.