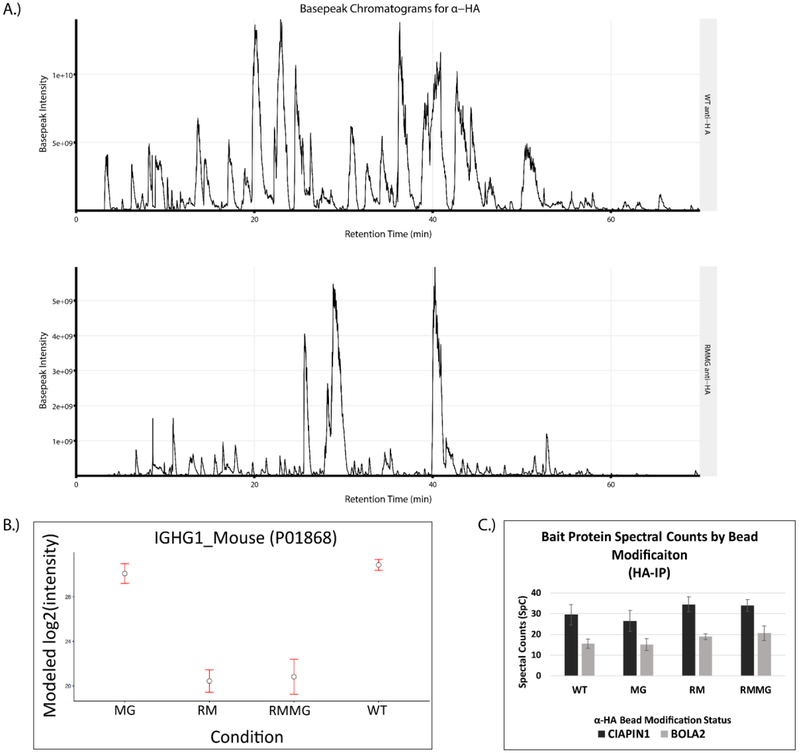
Figure 5:
The chemical derivatization method is extensible to antibody based affinity purification matrices. (A) Example basepeak chromatograms of a pair of pulldowns generated on WT (top) and derivatized (RMMG, bottom) α-HA beads. (B) IgG heavy chain protein intensity is dramatically reduced upon chemical derivatization of the beads prior to enzymatic digestion. The majority of signal reduction is granted by the reductive methylation and not the methylglyoxal treatment. Values are MSstats modeled protein intensities with error bars representing the 95% confidence interval. (C) α-HA beads retain binding of epitope tagged protein targets despite modification status. Confident spectral counts (SpC) shown for both of the bait proteins from their respective pulldowns. Each pulldown was acquired with two technical replicates on separate chromatographic columns. Values shown as the mean with error bars displaying the standard deviation.