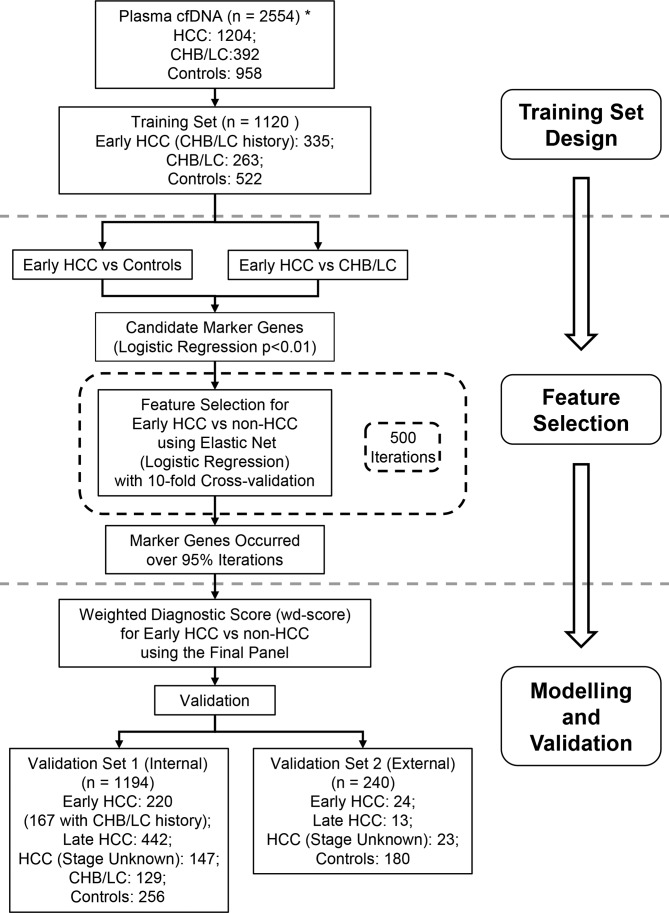
Figure 1.
Study design. The primary aim is to develop a 5hmC-based diagnostic model for early detection of HCC) using the genome-wide 5hmC-Seal profiles derived from plasma cfDNA. A two-step procedure is designed to identify a diagnostic model for early HCC (stage 0/A). The training set and the main validation set (‘validation set 1’) are comprised of HCC samples from Zhongshan Hospital of Fudan University and The Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital, Shanghai, China. An independent set of HCC samples from other participating hospitals (‘validation set 2’) are used to evaluate external performance of the 5hmC diagnostic model for HCC. Due to sample size limitation, only controls and patients with HCC are available in the external validation set. *The total number of study subjects does not include the 20 samples that were removed due to technical reasons. Control: healthy individuals and patients with benign liver lesions. CHB, chronic hepatitis B virus infection; cfDNA, cell-free DNA; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; 5hmC, 5-hydroxymethylcytosines; LC, liver cirrhosis.