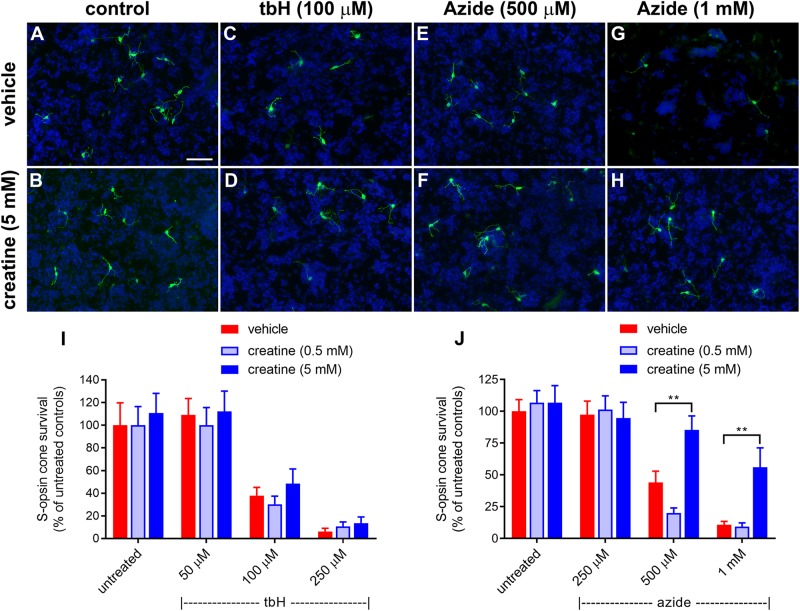
FIGURE 8.
Effect of creatine on stressor-induced S-opsin-labeled cone loss from mixed retinal cell cultures. Representative images from untreated (A), vehicle-treated (C,E,G) or creatine (5 mM)-treated (B,D,F,H) cultures additionally exposed to (C,D), 100 μM tbH (E,F), 500 μM sodium azide (G,H), 1 mM sodium azide. These data are followed by graphs quantifying the effect of creatine on tBH-induced (I) and sodium azide-induced (J) cone cell loss. It is evident that both tbH and sodium azide cause marked loss of S-opsin labeled cones in culture. It is further clear that although creatine has no effect on the cone loss induced by tbH, it is able to significantly protect these cells from sodium azide-induced toxicity. Values represent mean ± SEM, where n = 8 determinations from separate cultures. ∗∗P < 0.01, by one way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Scale bar, 50 μm.