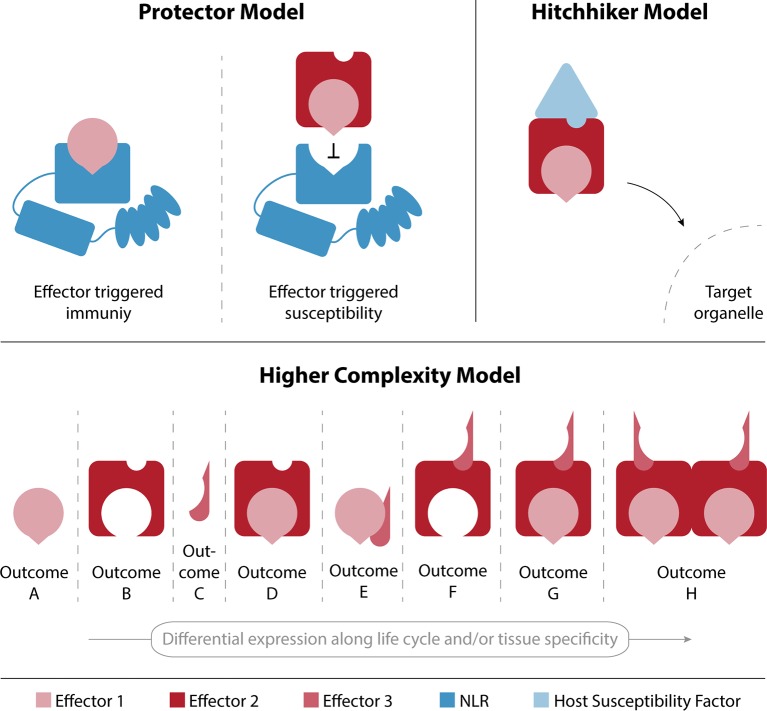
Figure 3.
Models for effector-effector interaction outcomes. The protector model describes an interaction between effectors 1 and 2, which results in the avoidance of recognition of effector 1 by the plant’s immune system and therefore leads to a successful infection. In the hitchhiker model, effector 1 is able to shuttle to its target organelle by interacting with effector 2, which in turn interacts with a plant susceptibility factor that mediates the shuttling upon effector binding. The higher complexity model highlights the plasticity that can emerge by differential effector expression along the pathogen’s lifecycle and/or in specific tissues.