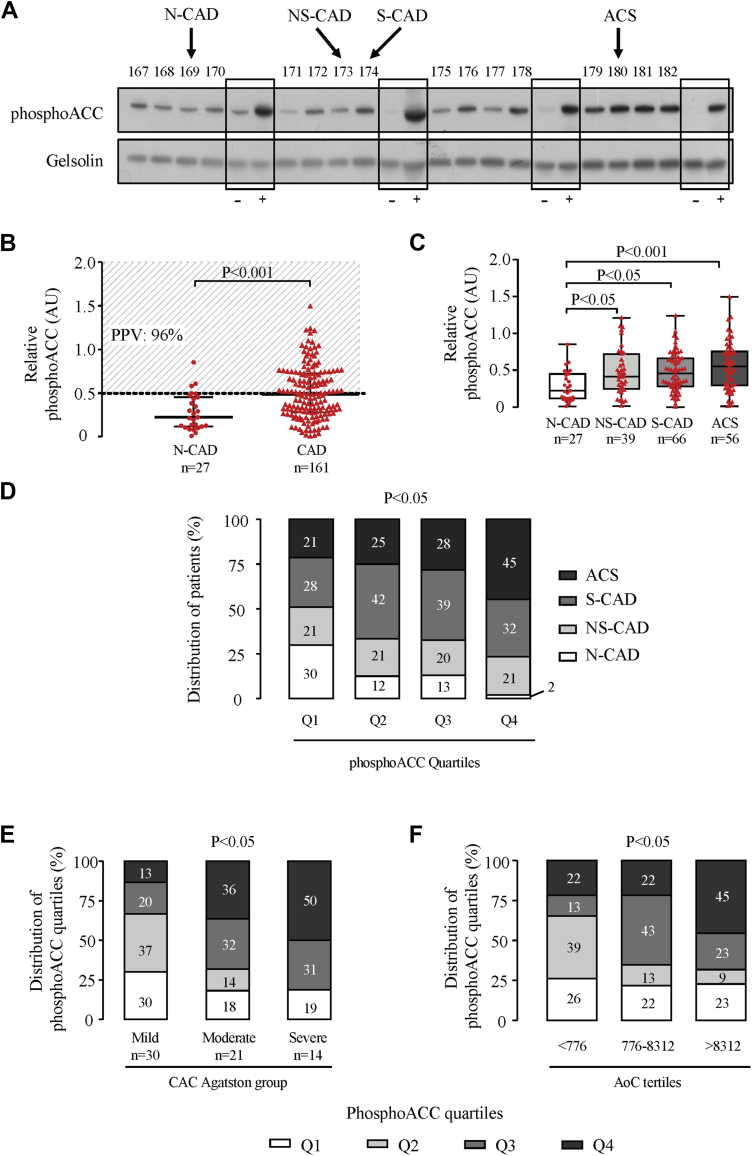
Figure 3.
PhosphoACC Correlates With Calcified Plaque Severity and Identifies High-Risk ACS Patients
(A) Representative Western blot of platelet acetyl-CoA carboxylase phosphorylation on serine 79 (phosphoACC) in 16 consecutive patients from the ACCTHEROMA trial, with negative control (–) corresponding to washed unstimulated platelets from healthy volunteers and positive control (+) corresponding to washed platelets from healthy volunteers stimulated with thrombin (0.5 U/ml) for 2 min. Four different controls are shown on the Western blot. (B) PhosphoACC quantification in N-CAD and CAD patients. Dotted line represents the threshold value of 0.5 arbitrary units (AU) estimated from receiver-operating characteristic curve analysis for discriminating between N-CAD and CAD patients. Positive predictive values (PPVs) of this threshold for CAD are indicated on the graph. Red dots (N-CAD, reference population) and triangles (CAD patients) represent individual values. Medians with interquartile range are presented. (C) Boxplot representation of platelet phosphoACC quantifications in N-CAD and CAD subgroups. (D) Clinical and angiographic characteristics of patients across the different quartiles of platelet phosphoACC. Distribution of platelet phosphoACC quartiles across (E) CAC Agatston score groups and (F) AoC score tertiles. The statistical differences between the groups were determined using the Mann-Whitney U test in B, Kruskal-Wallis test in C, and chi-square test in D to F. ACCTHEROMA = prospective evaluation of Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase phosphorylation state in platelets as a marker of atherothrombotic coronary and extra-coronary artery disease; M = molecular weight marker; Q = quartile; other abbreviations as in Figures 1 and 2.