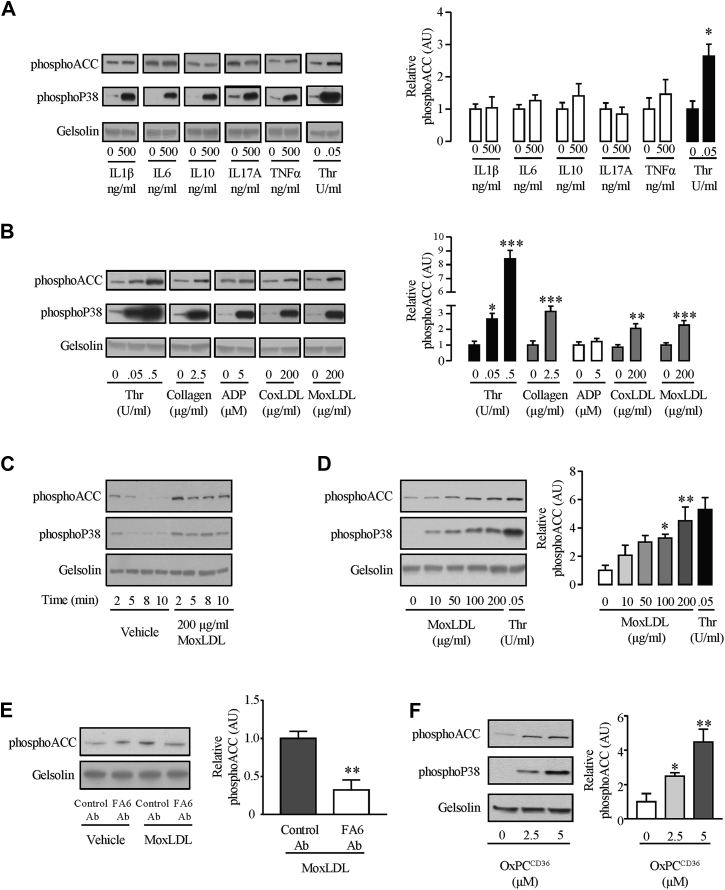
Figure 6.
Oxidized LDLs Induce Platelet phosphoACC in a CD36-Dependent Manner
Washed platelets (4.0 × 108/ml) from healthy volunteers were (A) treated with the following selected cytokines (interleukin-1beta [IL1β], IL-6, IL-10, IL-17A, and tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNFα]) and (B) stimulated with thrombin (Thr), collagen, adenosine diphosphate (ADP), copper-oxidized low-density lipoprotein (coxLDL) or myeloperoxidase-oxidized low-density lipoprotein (moxLDL) before lysis. (C) Time course and (D) dose-response curve of effect of moxLDL on phosphoACC. (E) Platelets were pretreated with 0.2 U/ml anti-CD36 antibody (FA6-152) (FA6 Ab) or an isotype control (control Ab) for 15 min before stimulation with moxLDL. (F) Platelets were stimulated with varying concentrations of a specific CD36 ligand (OxPCCD36) for 5 min before lysis. All experiments were carried out at least 4 times (biological replicates). Thr-stimulated platelets were used as a positive control. Gelsolin was the loading control. Representative Western blots are shown, with quantification of Western blots represented in the right-hand panels. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by (A, B, E) 2-tailed Student’s t-test or (B [Thr], D, F) 1-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni post hoc analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with unstimulated platelets. Ab = antibody; OxPCCD36 = oxidized choline glycerophospholipids; other abbreviations as in Figure 3.