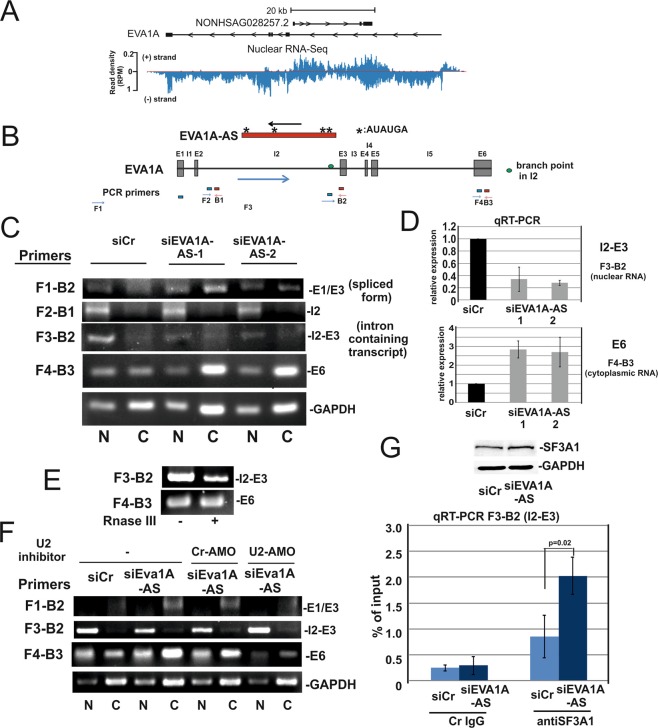
Figure 6.
EVA1A-AS suppressed EVA1A expression by inhibiting the splicing of intron 2 of EVA1A. (A) Nuclear RNA-Seq data (ENCFF760IDU) from HepG2 generated by the ENCODE Consortium were aligned to the reference human genome (GRCh38). SeqMonk was used to quantitate and visualize the data. (+) strand: EVA1A-AS; (−) strand: EVA1A. (B) Scheme of EVA1A and EVA1A-AS. Positions of PCR primers are indicated (blue forward; red backward). (C) HepG2 cells were transfected with siCr, siEVA1A-AS-1 or siEVA1A-AS-2. RNAs were isolated from nuclear [N] or cytoplasmic [C] fractions and supplied for RT-PCR or qRT-PCR (D) as indicated. (E) Nuclear RNA was isolated from HepG2 cells, incubated with shortcut RNase III, and RT-PCR was performed using F3-B2 and F4-B3 primers. (F) Sister cultures from (C) were treated with Cr-AMO or U2-AMO and RT-PCR was then performed as described in (C). (G) HepG2 cells were transfected with siCr and siEVA1A-AS. Cell extracts were supplied for SF3A1 specific immunoblot or were incubated with control IgG or anti SF3A1 antibody and then precipitated with Protein G Sepharose. Bound RNAs were analyzed by EVA1A, I2-E3 specific qRT-PCR.