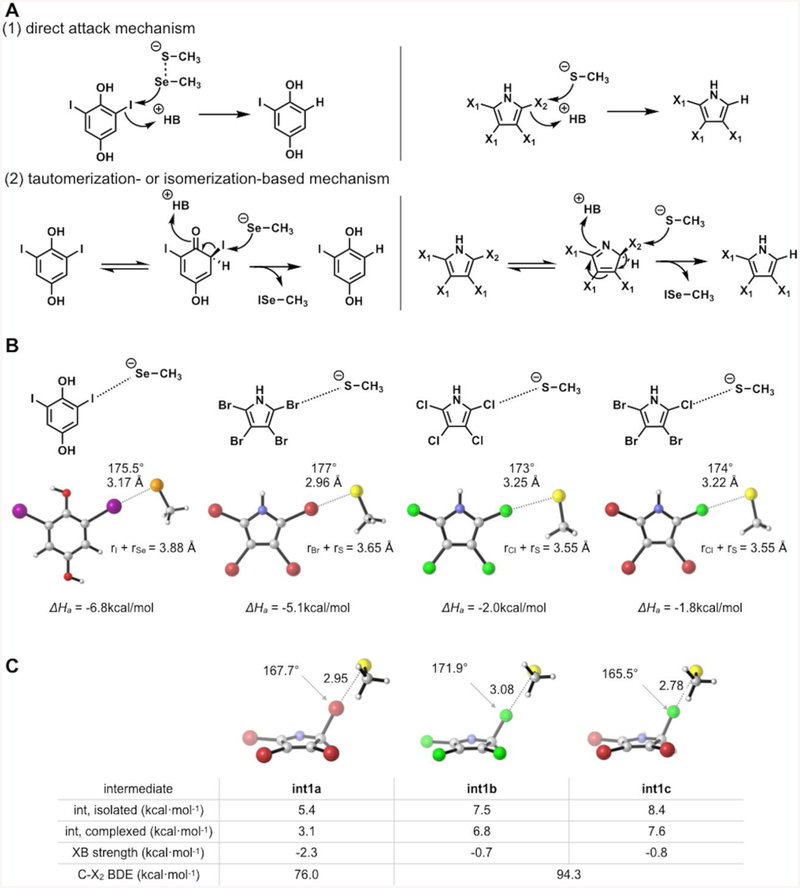
Figure 4.
(A) Possible mechanisms of dehalogenation by Dio (left) and Bmp8 (right). For tetrabromopyrrole, X1 = Br and X2 = Br. For tetrachloropyrrole, X1 = Cl and X2 = Cl. For 2-chloro-3,4,5-tribromopyrrole, X1 = Br and X2 = Cl. (B) Computed halogen bonding strengths for 2,6-diiodobenzene-1,4-diol-selenolate adduct (Dio) and tetrahalopyrrole-thiolate adducts (Bmp8). (C) Computed energies and halogen bond strengths of tetrahalo-2H-pyrrole intermediates and thiolate. Halogen atoms are colored as follows: purple is I, red is Br, and green is Cl.