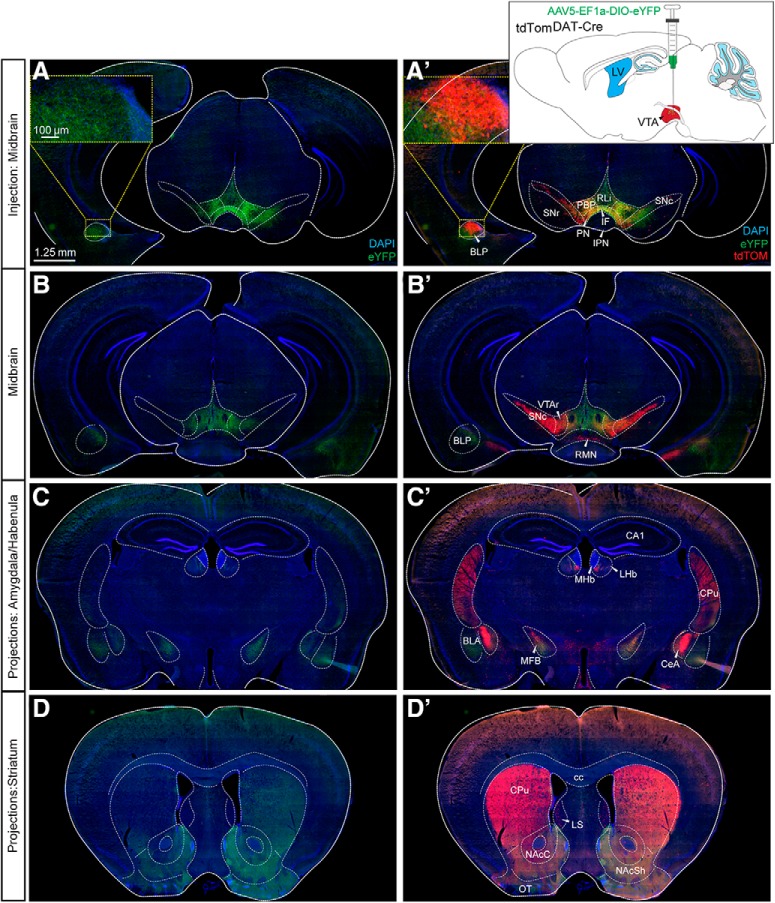
Figure 6.
Intracranial injection of AAV5-eYFP into the VTA of tdTomDAT-Cre mice verifies activity of Cre recombinase and enables identification of projections. A, A’, B, B’, Stereotaxic viral injections of AAV5-EF1a-DIO-eYFP into the VTA of tdTomDAT-Cre mice. Schematic illustration shows the injection site (A’). eYFP (A–D); eYFP and tdTOM (A’–D’). A, A’ and B, B’, Two different rostro-caudal levels of the midbrain. Cytoplasmic eYFP (green) detected in the VTA and some also in the SNc (A, B) with eYFP-positive projections detected in the BLP (in the section level shown in A). tdTOM-positive cells in VTA and SNc (A’, B’); also, the tdTOM-positive cell cluster shown in Figure 1 is detected in the BLP at the section level of A (A’; inset showing tdTOM-positive cell cluster and eYFP-positive fibers in the BLP, A’). C, C’, D, D’, eYFP-positive projections in additional target structures known for the VTA and SNc: the BLA and CeA of the amygdala and the habenula (C–C’), and the dorsal and ventral aspects of the striatum (D–D’). At this section level, TdTOM is detected in the CeA (scale bar: 1.25 mm; inset: 100 μm). See also Extended Data Figure 6-1. BLA, basolateral amygdala; CA1, CA1 region of hippocampus; cc, corpus callosum; CPu, caudate putamen; IPN, interpeducular nucleus; LS, lateral septum; LV, lateral ventricle; MFB, medial forebrain bundle; MHb, medial habenula; NAcSh, NAc shell; OT, olfactory tubercle; VTAr, VTA rostral part.