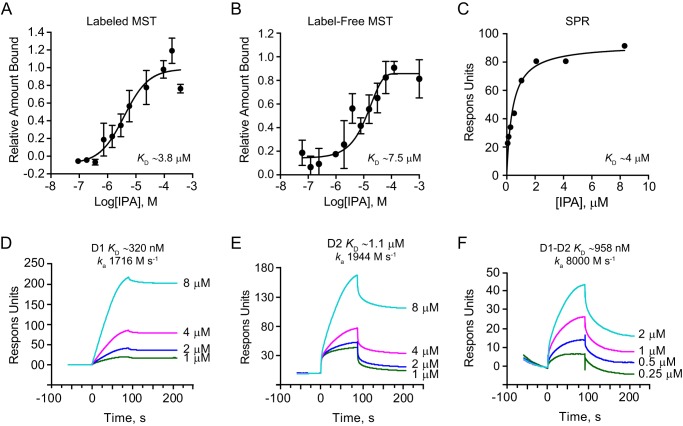
Figure 3.
Sec18-binding affinities for IPA. A, fluorescence MST of IPA binding to Sec18–His-8–labeled with Atto 488 Ni-NTA dye with fluorescence converted to fraction-bound M.O. affinity software and exported in Graphpad with KD of 3.84 ± 1.3 μm using log-inhibitor versus response four-parameter equation and error using S.E. (n = 3). B, label-free MST of IPA binding to unlabeled Sec18–His-8 converted to fraction bound as in Fig. 1A with KD of 7.4 ± 3.7 μm μm using log-inhibitor versus response four-parameter equation error using S.E. (n = 3). C, SPR of IPA to Sec18–His-8 linked to a Ni-NTA biosensor chip at ∼2000 RU with response measured subtracting blank reference cell and relevant blank injections. Data were exported from BiaEvaluate and into GraphPad and fit using a one-site specific binding model indicating a KD of ∼4 μm. D, SPR sensorgrams of Ni-NTA captured D1 of ∼2500 RU at corresponding PA injection concentrations with light blue 8 μm, magenta 4 μm, blue 2 μm, and green 1 μm exported from BiaEvaluate and into Graphpad for depiction. KD was measured by Kd/Ka 320 nm with ka of about 1700 m s−1. E, SPR sensorgrams of D2 to IPA as in Fig. 2D with KD ∼1.1 μm with ka of about 1900 m s−1. F, SPR sensorgrams of D1–D2 to IPA as in Fig. 2D with KD ∼960 nm and ka of about 8000 m s−1.