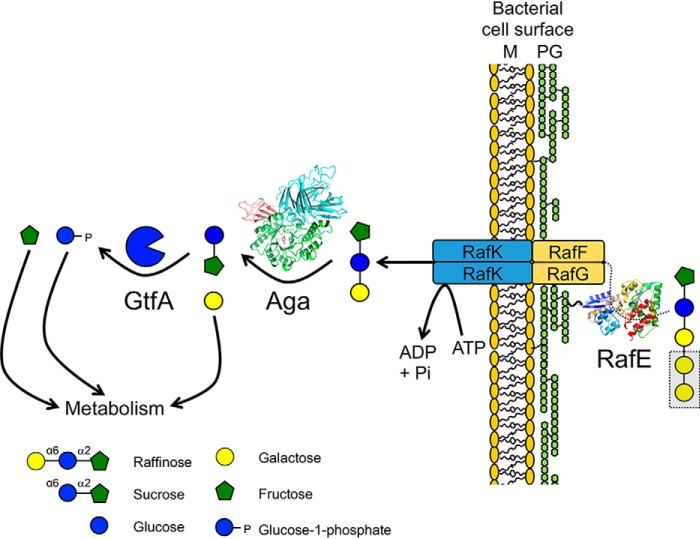
Figure 6.
Proposed pathway for RFO import and degradation in S. pneumoniae. The SBP RafE binds RFOs outside of the cell and delivers them to the membrane components of the ABC transporter (RafF and RafG). Powered by RafK (also known as MsmK), the RFOs are imported into the cytoplasm where they are sequentially degalactosylated by Aga. The released galactose can then enter metabolism either via the Leloir or tagatose-6-phosphate pathway (41). The remaining sucrose is cleaved by GtfA into fructose and G1P. Free fructose is likely phosphorylated by a fructokinase, such as ScrK (16), prior to entering glycolysis. G1P can be interconverted to glucose-6-phosphate by a phosphoglucomutase and enter either glycolysis or the pentose phosphate pathway (43). G1P is also an important intermediate in several pneumococcal anabolic pathways, including cell wall and capsule biosynthesis (42).