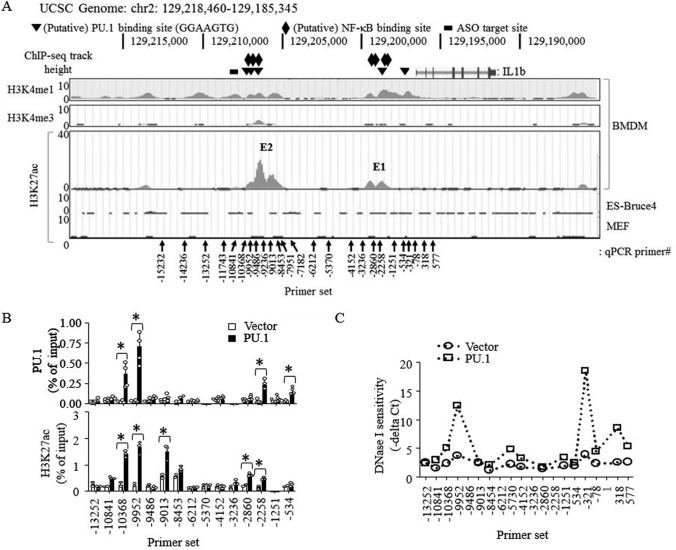
Figure 2.
Ectopically expressed PU.1 associates with distal IL-1β enhancer and proximal promoter regions and enhances H3K27ac levels and DNase I accessibility. A, screen snapshots of H3K4me1, and H3K4me3 ChIP-Seq signals in murine bone marrow–derived macrophages (BMDM; top two panels) and H3K27ac ChIP-Seq signals in bone marrow–derived macrophages, ES-Bruce4, and mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) (bottom panel) from the ENCODE-UCSC database. The black vertical arrows indicate locations where primers are targeting for qPCR analysis, and numerical values indicate locations of the first reverse primer nucleotide from the IL-1β TSS. The triangles show locations of putative PU.1-binding sites; the diamonds show locations of putative NF-κB–binding sites; the black bar indicates the target site of the GapmeR ASO. B and C, B16 cells were transfected with pcDNA3 (Vector) or pcDNA3-HA-PU.1 (PU.1) as described in the legend to Fig. 1. B, ChIP, using anti-PU.1 (top) or anti-H3K27ac (bottom), followed by qPCR using the primer sets indicated, was performed as described under “Experimental procedures.” Data are presented as percentage of enrichment with the precipitated target sequence compared with input DNA from two independent experiments. *, p < 0.05 (Student's t test). C, nuclei were prepared and digested using DNase I as described under “Experimental procedures.” Digested DNAs were then purified and analyzed by qPCR using the primer sets indicated. DNase I sensitivity was expressed as qPCR cycle threshold values subtracted from the cycle threshold values of nondigested nuclei.