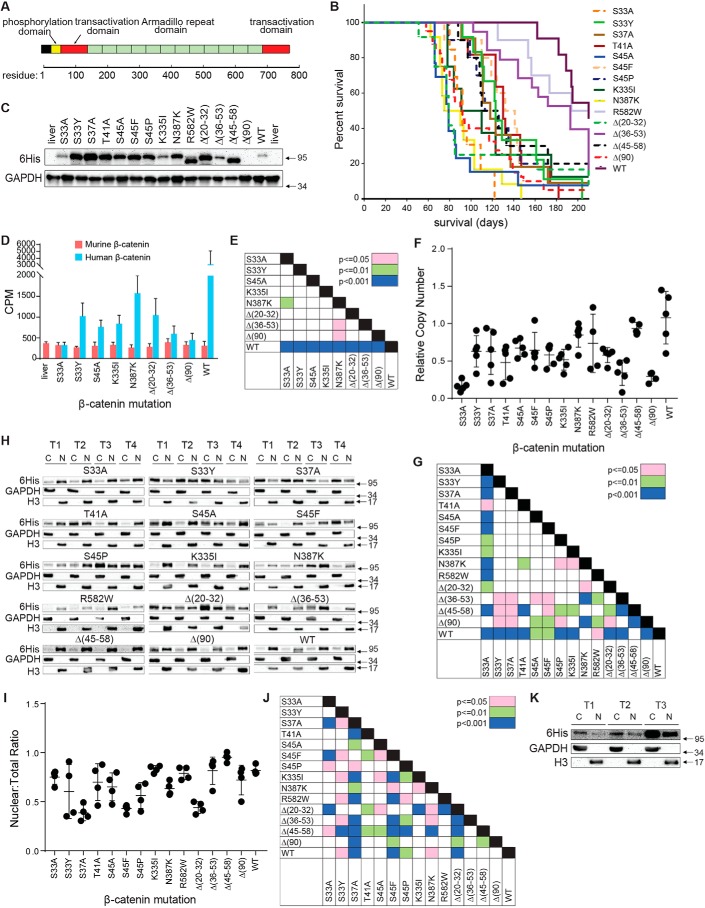
Figure 1.
Properties of tumors induced by β-catenin mutants. A, relevant landmarks in the β-catenin protein. The majority of the mutations described in the current report reside within the phosphorylation domain (approximately residues 30–50) (Table S1). The mutations N335I, N387K, and R582W are within the armadillo-repeat region that interacts with known partner proteins such as Tcf4, E-cadherin, and APC (45). B, Kaplan–Meier survival curves of mice with HBs driven by the indicated β-catenin mutants. Three tumor groups were identified based on differences in median survival (Fig. S1A). C, immunoblots of total β-catenin levels in whole-tumor lysates. See Fig. S2 for additional sets of tumors. Note that, because Δ(90) is Myc epitope–tagged rather than His6-tagged, it is not detected here. D, total transcript levels for human and murine β-catenin. Bars, mean levels from five individual livers or tumors ± S.E. (error bars). E, p values of each pair-wise comparison from the graph depicted in D. F, relative copy number of SB-β-catenin vectors stably integrated into tumor DNAs from each of the indicated tumor groups. Copy numbers were determined using a TaqMan-based assay and were normalized to the nuclear gene encoding apolipoprotein B. G, p values for all pair-wise comparisons shown in F. H, nuclear:cytoplasmic distribution of β-catenin mutants and WT β-catenin in tumors. Four tumors (T1–T4) were evaluated for each mutant. Except for Δ(90), which was detected with an anti-Myc antibody, all β-catenins were detected with an anti-His6 tag antibody. C, cytoplasmic fraction; N, nuclear fraction. I, quantification of the proportion of β-catenin from F that is nuclear. 4–6 tumors from each group were used to obtain the results. J, p values for all pair-wise comparisons shown in I. K, WT β-catenin localizes mostly to the cytoplasm in rapidly growing Δ(90) tumors. Mice were co-injected with equivalent amounts of SB vectors encoding Myc epitope–tagged Δ(90) β-catenin and His6 epitope–tagged WT β-catenin. The resulting tumors, all of which appeared rapidly (Group 1) (B), were fractionated as described in H.