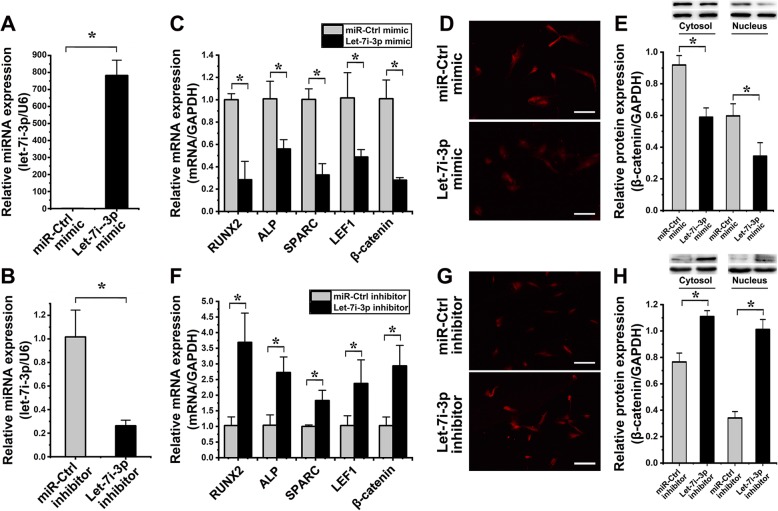
Fig. 8.
Let-7i-3p modulates the osteogenic differentiation of hASCs under cyclic strain (*p < 0.05, significant differences existed between these two groups). a Transfection efficiency detected by qPCR. The expression of let-7i-3p in hASCs transfected with the let-7i-3p mimic was increased 776.40 ± 111.78-fold (p < 0.001). b The expression of let-7i-3p in hASCs transfected with the let-7i-3p inhibitor was decreased 3.88 ± 0.11-fold (p = 0.005). c The effect of let-7i-3p overexpression on the osteogenic differentiation of hASCs under cyclic strain as determined by qPCR. Compared to those in the miR-Ctrl mimic group, the levels of the following mRNA markers in hASCs transfected with the let-7i-3p mimic were significantly decreased: RUNX2 (3.52 ± 1.94-fold, p = 0.002), ALP (1.80 ± 0.15-fold, p = 0.012), SPARC (3.07 ± 0.86-fold, p < 0.001), LEF1 (2.08 ± 0.73-fold, p = 0.018), and β-catenin (3.60 ± 0.57-fold, p = 0.002). d The immunofluorescence intensity of β-catenin in the nucleus was weakened in hASCs transfected with the let-7i-3p mimic (scale bar 100 μm). e The expression of cytoplasmic and nuclear β-catenin in hASCs transfected with the let-7i-3p mimic significantly respectively decreased 1.56 ± 0.06-fold (p = 0.002) and 1.74 ± 0.24-fold (p = 0.019) than those in the miR-Ctrl mimic group. f The effect of let-7i-3p suppression on the osteogenic differentiation of hASCs under cyclic strain as determined by qPCR. Compared to those in the miR-Ctrl inhibitor group, the levels of the following mRNA markers in hASCs transfected with the let-7i-3p inhibitor were significantly increased: RUNX2 (3.58 ± 0.82-fold, p = 0.009), ALP (2.53 ± 0.49-fold, p = 0.008), SPARC (1.83 ± 0.28-fold, p = 0.012), LEF1 (2.31 ± 1.03-fold, p = 0.046), and β-catenin (2.86 ± 1.68-fold, p = 0.010). g The immunofluorescence intensity of β-catenin in the nucleus was enhanced in hASCs transfected with the let-7i-3p inhibitor (scale bar 100 μm). h The expression of cytoplasmic and nuclear β-catenin in hASCs transfected with the let-7i-3p inhibitor significantly respectively increased 1.45 ± 0.11-fold (p = 0.003) and 2.97 ± 0.19-fold (p = 0.001) than those in the miR-Ctrl inhibitor group