Abstract
Background
Persistent infection with human papillomaviruses (HPVs) has been associated with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical cancer. However, why only a fraction of HPV cases progress to cancer is still unclear.
Methods
We focused on the heterogeneity, classification, evolution and dispersal of variants for 14 common HPV types in 262 HPV-positive patients with cervical lesions. The E6 and E7 genes of HPV were sequenced and compared with the HPV reference for sequence analysis. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the neighbour-joining tree method with MEGA 7.0.
Results
In this study, 233 E6 and 212 E7 sequences were successfully amplified by PCR, and these sequences were divided into 5 species groups: alpha-9 (HPV16, 31, 33, 52, 58), alpha-5 (HPV51), alpha-6 (HPV53, 66), alpha-7 (HPV18, 39, 59, 68) and alpha-10 (HPV6, 44). The incidence of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) in patients infected with alpha-9 HPV was significantly increased compared with other groups (P < 0.0001), especially HPV16 (P < 0.0001). Strikingly, E7 had significantly fewer nonsynonymous variants in the HSIL compared to <HSIL groups (P = 3.17× 10− 4). The A388C (K93 N) variation in HPV58 E6 can significantly reduce the risk of HSIL (P = 0.015). However, T7220G (D32E) variation in HPV16 E6 and A7689G (N29S) in HPV16 E7 increased the incidence of HSIL compared to the <HSIL group (P = 0.036 and 0.022).
Conclusions
Strict conservation of E7 is important for HPV carcinogenicity, especially N29 of HPV16. The findings in this work provide preventative/therapeutic interventions for HPV infections and CIN.
Keywords: Human papillomavirus, Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, E6 and E7 gene, Genetic variations, Polymorphism analysis
Background
Currently, over 200 types of HPV have been fully characterized, of which the great majority clusters phylogenetically within three genera of the Papillomaviridae family: alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) [1]. The α genus contains HPV types that infect mostly mucosal and genital regions, including 65 papillomavirus types from humans, and this group of viruses constitutes 14 species groups [2]. Persistent HPV infections are considered the material cause of cervical cancer, where greater than 99% of cervical cancer lesions contain HPV DNA [3]. At least 3 ancestral papillomaviruses are responsible for the current heterogeneous groups of genital HPV genomes, including low-risk (LR)1 (α1, 8, 10 and 13), LR2 (α2, 3, 4 and 14) and high-risk (HR) (α5, 6, 7, 9 and 11) [2].
However, why only a small proportion of HPV infections progressed to precancer and cancer is unclear [4]. In addition to the pathogenic heterogeneity of distinct HPV types, previous studies indicate that HPV variants are also associated with different risks of cancer progression. For example, the HPV16 variant has significantly different risks of HPV persistent infection, progression to cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical cancer [5, 6]. Lisa Mirabello observed that compared to the most frequent A1/A2 sublineages, the A4, C, D2 and D3 sublineages conferred a higher hazard of CIN and cervical cancer [7]. The C variant (vs. B variant) of HPV52 was associated with an increased prevalence of cytologically diagnosed and histologically confirmed HSIL or worse lesions [8]. These data indicate that HPV variants have different phenotypic characteristics, including carcinogenicity.
HPV E6 and E7 are the major oncogenes, which are highly expressed in tumours and are related to inducing cellular immortalization, transformation, and carcinogenesis through protein–protein interactions with tumour suppressor proteins [9]. For example, E6 binds the conserved LxxLL consensus sequences of the ubiquitin ligase E6-associated protein (E6-AP), which works as a connecting bridge between E6 and p53, leading to its subsequent degradation [10]. Similarly, E7 targets and promotes the inactivation of RB1, thus inducing cell-cycle progression through activation of E2F-driven transcription [11].
In this study, we focused on the phylogeny and polymorphism of E6 and E7 gene variants for 14 common HPV types (HPV16, 31, 33, 52, 58, 51, 53, 66, 18, 39, 59, 68,6, 44) in Shanghai women with cervical lesions. This comprehensive analysis will help us understand the clinical and biological role of sequence variation.
Materials and methods
Study population
In total, 262 HPV-positive patients (mean age 38.34 ± 10.52 years, 21–78) with histopathologically confirmed cervical lesions, including 92 nonneoplastic, 69 low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) and 101 high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL), were recruited from the Cervical Disease Centre at the Shanghai First Maternity and Infant Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine in Shanghai, China. Histopathological findings are divided into certain groups as nonneoplastic (chronic cervicitis and inflammation-related regenerative changes), LSIL (CIN I/mild dysplasia), HSIL (CIN II and CIN III/moderate and severe dysplasia) and invasive carcinoma. CIN I refers to mildly atypical cellular changes in the lower third of the epithelium, CIN II refers to moderately atypical cellular changes confined to the basal two-thirds of the epithelium (formerly called moderate dysplasia) with preservation of epithelial maturation. CIN III refers to severely atypical cellular changes encompassing greater than two-thirds of the epithelial thickness and includes full-thickness lesions (previous terms were severe dysplasia or carcinoma in situ).
The criteria for the inclusion of patients enrolled into their current study: HPV single infection; Histopathologically confirmed by Colposcopy biopsy. The exclusion: Co-infected with different HPV types; Not histopathologically confirmed; the patients with vaginitis or other bacterial/virus infection.
Genomic DNA isolation and HPV typing
DNA from exfoliated cervical cells was extracted using the TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit (No: 3304–9) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. HPV genotyping was conducted using an HPV GenoArray Test Kit (HybriBio Ltd).
Amplification and sequencing
After HPV testing, the remaining DNA samples were stored at − 80 °C and used to amplify E6 and E7 using specific primers (Table 1). Subsequently, PCR products excised from 1.5% agarose gel were sequenced bidirectionally by SAIYIN Gene Biotechnology Company, Shanghai, China.
Table 1.
Primers used for the molecular characterization of fourteen human papillomavirus E6 and E7 genes
| HPV genotype | Reference sequence ID | Gene | Direction | Sequence 5′-3’ | Primer position | Product size, bp | Annealing Temperature, °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | KU298876.1 | E6, E7 | Forward | AGGGACCGAAAACGGTTCAA | 32 | 1079 | 58 |
| Reverse | CTAACATATGGACTACCTAAAT | 1110 | |||||
| 16 | NC_001526 | E6 | Forward | ACCGTTTTGGGTTACACATTTAC | 6996 | 700 | 60 |
| Reverse | CTGTCATTTAATTGCTCATAACAGTAGA | 7695 | |||||
| E7 | Forward | CATTAGAACAGCAATACAACAAACC | 7405 | 579 | 60 | ||
| Reverse | TCCACTACAGCCTCTACATAAAACC | 7983 | |||||
| 18 | NC_001526 | E6, E7 | Forward | CATGTCCAACATTCTGTCTACCC | 7751 | 1064 | 58 |
| Reverse | TTACAACCCGTGCCCTCC | 957 | |||||
| 31 | J04353.1 | E6, E7 | Forward | AGTAGGGAGTGACCGAAAGTGG | 27 | 959 | 58 |
| Reverse | CACTACTGTCTTCATTTTCGTCCTC | 985 | |||||
| 33 | M12732.1 | E6, E7 | Forward | AACTATGCCTTGTAAAAGTGAGTCAC | 7813 | 1116 | 58 |
| Reverse | TAAATCCGTGCCACTGTCATC | 1015 | |||||
| 39 | M62849.1 | E6, E7 | Forward | AAGGGAGTAACCGAAAACGG | 34 | 1096 | 58 |
| Reverse | CCTGTGCTGTCTCACGCTCT | 1129 | |||||
| 44 | U31788.1 | E6, E7 | Forward | ATCGGTTGACACACACCCTG | 7796 | 1083 | 58 |
| Reverse | CATCCGCCTCCTGTCGTTTAACAA | 1045 | |||||
| 51 | KU298901.1 | E6, E7 | Forward | ACTAGGGTGTAACCGAAAAGGG | 17 | 965 | 58 |
| Reverse | TCATCCTCATCATCCGAAACAT | 981 | |||||
| 52 | NC_001592.1 | E6 | Forward | ACCGTACCCACAACCACTTTT | 7929 | 738 | 58 |
| Reverse | TTGTGGCTTGTTCTGCTTGTC | 706 | |||||
| E7 | Forward | AACGCCATTATGTCCTGAAGAA | 422 | 554 | 58 | ||
| Reverse | CATCCTCGTCCTCTGAAATGTTAT | 975 | |||||
| 53 | GQ472849.1 | E6, E7 | Forward | AGACAGGGAGTAACCGAAATAGG | 24 | 988 | 58 |
| Reverse | GCTTTCCTCGTCTGTTTCATCTT | 1011 | |||||
| 58 | D90400 | E6 | Forward | CGTTTTGGGTCACATTGTTCA | 7782 | 702 | 58 |
| Reverse | CATAATTGCTCATAGCAGAATAGGTC | 659 | |||||
| E7 | Forward | TTCGCTATATGGAGACACATTAGAA | 352 | 613 | 58 | ||
| Reverse | TTCTTCGTTCTATTACCGCTTCTA | 964 | |||||
| 59 | X77858.1 | E6, E7 | Forward | AAGCAACCGAAAAAGGTCGG | 7805 | 1128 | 58 |
| Reverse | TGTGGTATCATCAATAAAATCTACC | 1036 | |||||
| 66 | U31794.1 | E6, E7 | Forward | TTGGGAGTAACCGAAATGGG | 27 | 992 | 58 |
| Reverse | CATTCTCCTCCTCGCTTTCAT | 1018 | |||||
| 68 | DQ080079 | E6, E7 | Forward | CCGAAAAAGGTTGGGCACAC | 7682 | 1098 | 58 |
| Reverse | TGAACCTGTATCTGTTGCGTT | 958 |
HPV Human papillomavirus
Phylogenetic tree analysis and sequence analysis
The neighbour-joining phylogenetic tree of the HPVs was constructed by MEGA 7.0 using the maximum composite likelihood estimate [12]. To construct distinct phylogenetic branches, the reference HPV sequences were obtained from the GenBank database. The phylogenetic trees were visualised in FigTree v1.4.3 and online Evolview [13, 14].
The sequences were subsequently analysed by NCBI Blast, and all unique sequences were compared pairwise using the ClustalW tool of MEGA 7.0. The nucleotide positions of HPV were numbered on the basis of the reference sequence KU298876.1 (HPV6), NC_001526 (HPV16), NC_001526 (HPV18), J04353.1 (HPV31), M12732.1 (HPV33), M62849.1 (HPV39), U31788.1 (HPV44), KU298901.1 (HPV51), NC_001592.1 (HPV52), GQ472849.1 (HPV53), D90400 (HPV58), X77858.1 (HPV59), U31794.1 (HPV66), and DQ080079 (HPV68).
Statistical analysis
Fisher’s exact test was chosen for statistical analysis. P < 0.05 was used as the threshold to indicate statistical significance. All the P values in the present study were two-sided. The power calculation was performed by G*power software [15].
Results
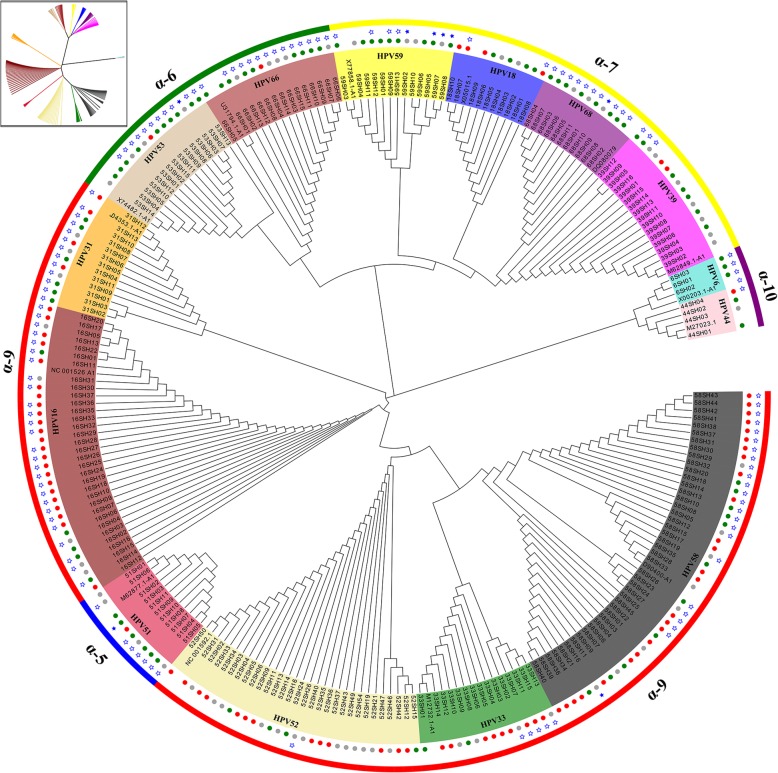
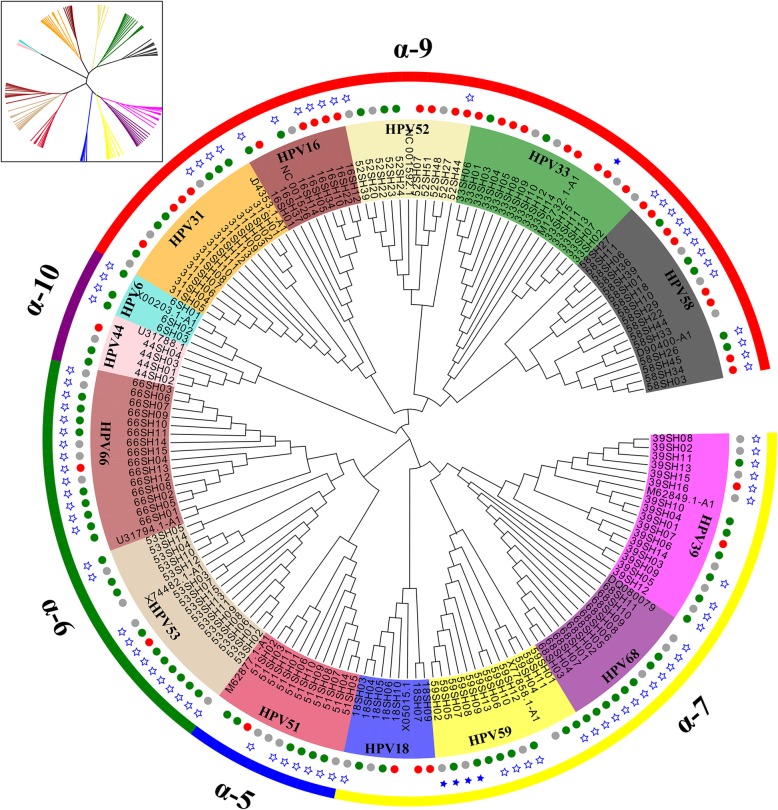
In this study, total DNA was extracted from exfoliated cervical cell samples from 262 HPV-positive patients. In total, 233 E6 and 212 E7 sequences were successfully amplified by PCR. Based on the reference sequences, we confirmed that these sequences were divided into 14 types of HPV (16, 31, 33, 52, 58,51,53, 66,18, 39, 59, 68, 6, 44) and 5 species groups (alpha-5, alpha-6, alpha-7, alpha-9, alpha-10) using phylogenetic tree analysis, where alpha-10 was a low-risk (LR) clade (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2).
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic tree of Alphapapillomavirus based 233 nucleotide sequence alignments of HPV E6. The maximum likelihood tree was constructed using MEGA7.0. Phylogenetic trees were visualised in FigTree v1.4.3 and Evolview. These sequences were divided into 5 species groups (alpha-5, alpha-6, alpha-7, alpha-9, alpha-10), of which alpha-10 was a low-risk (LR) clade. Green, grey and red circle represent cervicitis, low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, respectively; the star represents nonsynonymous mutation, and blue stars are insertion/deletions
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic tree of Alphapapillomavirus based 156 nucleotide sequence alignments of HPV E7. The maximum likelihood tree was constructed using MEGA7.0. Phylogenetic trees were visualised in FigTree v1.4.3 and Evolview. These sequences were divided into 5 species groups (alpha-5, alpha-6, alpha-7, alpha-9, alpha-10), of which alpha-10 was a low-risk (LR) clade. Green, grey and red circle represent cervicitis, low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, respectively; the star represents nonsynonymous mutations, and blue stars are insertion/deletions
Table 2 shows the distribution of the sublineage-specific infections for individual types in cervicitis, LSIL and HSIL groups. The incidence of HSIL was significantly increased in patients infected with alpha-9 HPV compared with other species (P < 0.0001), especially HPV16 (P < 0.0001). There was no statistically significant difference in the severity of CIN for all types of lineages. For HPV16, 37.5% HPV16 A1–3 sub-lineage caused HSIL, as well as 75.9% A4. Among 54 determinable samples of HPV 52, the A, B and C variants were found in 1 (1.85%), 52 (96.3%) and 1 (1.85%) samples, respectively, and lineage B was the most common. Among 45 determinable samples of HPV 58, sublineages A1, A2 and A3 variants were found in 57.8, 22.2 and 17.8% of all HPV58 samples, respectively. The nonprototype-like variant (sublineage B1) of HPV58 was rare in our study. A2 (69.23%, 9/13) and A1 (66.67%, 10/15) were common sublineages for HPV31 and HPV33, respectively.
Table 2.
Distribution of lineage-specific human papillomavirus infections in samples from Shanghai
| Age# | Lineage or | Women | pathologic diagnosis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Type | (Mean±SD) | sublineage | N | IF | LSIL | HSIL | P* Value |
| α-9 | 164 | 34 | 39 | 91 | <0.0001a | |||
| 16 | 34.88 ± 6.15 | A1-3 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 0.083 | |
| 35.10 ± 6.83 | A4 | 29 | 2 | 5 | 22 | |||
| 31 | 33.33 ± 8.41 | A2 | 9 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 0.108 | |
| B2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| 31.67 ± 5.51 | C2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 33 | 38.90 ± 11.57 | A1 | 10 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 0.417 | |
| A2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| 39.75 ± 8.18 | A3 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 3 | |||
| 52 | A | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 38.48 ± 11.83 | B | 52 | 10 | 17 | 25 | |||
| C | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| 58 | 40.19 ± 9.55 | A1 | 26 | 7 | 4 | 15 | 0.862 | |
| 40.30 ± 7.54 | A2 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 6 | |||
| 44.25 ± 14.44 | A3 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 4 | |||
| B1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| α-5 | 11 | 6 | 4 | 1 | ||||
| 51 | A1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.532 | ||
| 36.50 ± 7.94 | A2 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 39.83 ± 14.68 | A4 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 | |||
| α-6 | 30 | 19 | 9 | 1 | ||||
| 53 | 34.00 ± 5.66 | A1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.588 | |
| 42.50±12.02 | B1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |||
| 33.33±10.41 | C1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
| 31.00 ± 7.07 | D1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |||
| 36.00 ± 13.36 | D3 | 6 | 5 | 0 | 1 | |||
| 66 | A1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.552 | ||
| 45.17 ± 13.53 | B1 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 42.50 ± 13.18 | B2 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 0 | |||
| α-7 | 50 | 28 | 16 | 6 | ||||
| 18 | 34.50 ± 10.42 | A1 | 10 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 0.4 | |
| 39 | 39.08 ± 10.49 | A1 | 13 | 5 | 6 | 2 | 1 | |
| 43.00 ± 22.63 | A2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |||
| B1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 5 | 33.50 ± 8.96 | A1 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0.664 | |
| 36.00±2.65 | A3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 36.50±6.36 | B1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |||
| 51.25 ± 5.00 | B1-2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 | |||
| 68 | 45.00 ± 10.90 | C1 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 1 | |
| 35.00 ± 8.49 | C2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |||
| α-10 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 6 | 34.33 ± 12.06 | B1 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 44 | 32.50 ± 4.04 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Total | 262 | 92 | 69 | 101 | <0.0001b | |||
IF Cervicitis, LSIL Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, HSIL, High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; aComparison of types within α-9 group; bComparison between Genus; *P values remain significant after Bonferroni adjustment for multiple tests. #P<0.05 using analysis of variance. The boldface entries indicate the distribution of α-5, α-6, α-7, α-9 and α-10 HPV infection in different populations (IF, LSIL and HSIL group)
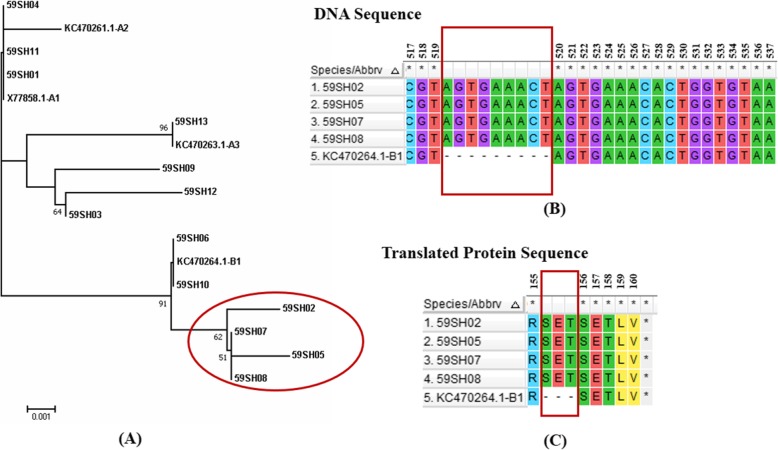
Interestingly, we observed that one variant represented four out of 13 HPV59-positive samples that appeared to form a new candidate, sublineage B1–2 (Fig. 3a). A 9-base sequence (AGTGAAACT) was inserted after position 519 of the E6 sequence, and 9 inserted bases were translated into 3 amino acids SET (Fig. 3b and c). These diagnostic SNPs were unique to the B1–2 sublineage.
Fig. 3.
Phylogenetic tree and schematic representation of 4 novel HPV59 E6 variants. a Phylogenetic tree of the HPV59 variants based on E6 sequences. b An insertion (AGTGAAACT) at nucleotide sites 519 in 4 variants. c The insertion sequence was translated into SET. Four variants are marked by red circles
Nonsynonymous mutations for the E6 and E7 genes within all types of HPV were evaluated. The A burden test was used to determine if the variant distribution was different between the IF, LSIL and HSIL groups by viral region (Table 3, Fig. 1, and Fig. 2). Despite nearly equal numbers of E6 and E7 sequences among three groups (IF, 159; LSIL, 121; HSIL, 165), the IF group overall had a significantly higher number of variants compared to the LSIL and HSIL groups (P = 3.83× 10− 4). Strikingly, the E7 gene had significantly fewer nonsynonymous variants in the HSIL compared to LSIL and IF groups (P = 3.17× 10− 4).
Table 3.
Rare variant burden analysis for nonsynonymous variants within all types of HPV for the cervicitis, LSIL and HSIL groups
| N Controls | N LSIL | N HSIL | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viral | Number | with | % of | Number | with | % of | Number | with | % of | |
| Gene | IF | Variants | Controls | LSIL | Variants | Controls | HSIL | Variants | Controls | P Value |
| E6 | 86 | 55 | 64.0 | 63 | 32 | 50.8 | 84 | 45 | 53.6 | 0.215 |
| E7 | 73 | 53 | 72.6 | 58 | 31 | 53.4 | 81 | 32 | 39.5 | 3.17 × 10–4* |
| Total | 159 | 108 | 67.9 | 121 | 63 | 52.1 | 165 | 77 | 46.7 | 3.83 × 10–4* |
HPV Human papillomavirus; IF cervicitis; LSIL low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; HSIL high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion;*P values remain significant after Bonferroni adjustment for multiple tests
Moreover, we confirmed that the incidence of HSIL in patients infected with the alpha-9 HPV group was significantly increased compared with the other groups (P < 0.0001). We then further analysed nonsynonymous mutations of the alpha-9 HPV (HPV16, 31, 33, 52, 58) E6 and E7 genes in the HSIL case and control groups (Table 4). In the case group, 13 variations were observed in the E6 gene, and 19 mutations were observed in the E7 gene. In the control group, 17 and 14 variations were found in the E6 and E7 genes, respectively. For HPV16, the distribution of T7220G (D32E) variation in E6 and A7689G (N29S) in E7 showed a different trend between the case group and control group (P = 0.036 and 0.022) (Table 4), power (1-β) 0.562 and 0.629. For HPV58, A388C (K93 N) variation can significantly reduce the risk of HSIL and was a protective factor (P = 0.015), power (1-β) 0.624. In the remaining three types of alpha-9 HPV, no significant differences in the distribution of other variations between the case group and the control group were found. In addition, we performed co-variation analysis of five HPVs E6 and E7 genes in the α-9 group. But there was no significant correlation between E6 and E7 covariation and cervical lesions (Additional file 1: Table S1).
Table 4.
HPV E6/E7 gene variations and amino acid substitutions in the case and control groups
| HPV | Genome | Amino | Caseb | Controlc | P value* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| positiona | acida | Mutation | Frequency(%) | Mutation | Frequency (%) | ||
|
HPV16 E6 case (n=23) control (n=10) |
T7179G | L19V | 1 | 4.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 |
| T7220G | D32E | 20 | 87.0 | 5 | 50.0 | 0.036 | |
| C7377T | H85Y | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 10.0 | 0.303 | |
| G7384C | C87S | 2 | 8.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 | |
| A7404T | T94S | 3 | 13.0 | 1 | 10.0 | 1.000 | |
| A7484C | E120D | 1 | 4.3 | 1 | 10.0 | 0.521 | |
|
E7 case (n=21) control (n=10) |
A7688C | N29H | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 10.0 | 0.323 |
| A7689G | N29S | 19 | 90.5 | 5 | 50.0 | 0.022 | |
| C7832T | R77C | 1 | 4.8 | 1 | 10.0 | 1.000 | |
|
HPV31 E6 case (n=4) control (n=9) |
C285T | H60Y | 0 | 0.0 | 3 | 33.3 | 0.497 |
| A297G | T64A | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 11.1 | 1.000 | |
| A475G | K123R | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 11.1 | 1.000 | |
| C520T | A138V | 0 | 0.0 | 4 | 44.4 | 0.228 | |
|
E7 case (n=4) control (n=9) |
C626T | H23K | 4 | 100.0 | 6 | 66.7 | 0.497 |
| G695A | E46K | 0 | 0.0 | 4 | 44.4 | 0.228 | |
| A743G | K62E | 4 | 100.0 | 9 | 100.0 | — | |
|
HPV33 E6 case (n=9) control (n=6) |
A213C | K35N | 3 | 33.3 | 2 | 33.3 | 1.000 |
| A364C | N86H | 3 | 33.3 | 2 | 33.3 | 1.000 | |
| A387C | K93N | 3 | 33.3 | 1 | 16.7 | 0.604 | |
| A446G | Q113R | 3 | 33.3 | 1 | 16.7 | 0.604 | |
|
E7 case (n=9) control (n=6) |
A834G | N88D | 1 | 11.1 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 |
| C850A | T93N | 1 | 11.1 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 | |
| A862T | Q97L | 3 | 33.3 | 2 | 33.3 | 1.000 | |
|
HPV52 E6 case (n=13) control (n=17) |
G108C | E3Q | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 5.9 | 1.000 |
|
E7 case (n=27) control (n=26) |
C624G | C24W | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.8 | 0.491 |
| C662T | T37I | 1 | 3.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 | |
| G707A | S52D | 1 | 3.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 | |
| T727G | Y59D | 1 | 3.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 | |
| C733T | H61Y | 1 | 3.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 | |
| G742A | D64N | 1 | 3.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 | |
| T848G | L99R | 1 | 3.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 | |
|
HPV58 E6 case (n=25) control (n=18) |
G203C | E32Q | 3 | 12.0 | 1 | 5.6 | 0.628 |
| C228T | S40F | 1 | 4.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 | |
| C367A | D86E | 2 | 8.0 | 2 | 11.1 | 1.000 | |
| A388C | K93N | 1 | 4.0 | 6 | 33.3 | 0.015 | |
| A544T | K145S | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 5.6 | 0.419 | |
|
E7 case (n=12) control (n=9) |
C632T | T20I | 3 | 25.0 | 3 | 33.3 | 1.000 |
| G694A | G41R | 3 | 25.0 | 2 | 22.2 | 1.000 | |
| C755A | T61N | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 11.1 | 0.429 | |
| G760A | G63S | 4 | 33.3 | 2 | 22.2 | 0.659 | |
| G761A | G63D | 3 | 25.0 | 2 | 22.2 | 1.000 | |
| A793G | T74A | 1 | 8.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 | |
| C801A | D76E | 1 | 8.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 | |
| T803C | V77A | 0 | 0.0 | 3 | 33.3 | 0.063 | |
HPV Human papillomavirus; aThe reference HPV16/31/33/52/58 E6/E7 gene sequence was NC_001526, J04353.1, M12732.1, NC_001592.1, and D90400. bHSIL group, cLSIL and IF group. * Fisher's exact test P value, and the bold numbers refer P value less than 0.05
Discussion
Persistent infection with HPV is the most important risk factor for cervical cancer [16]. According to their oncogenic potential, HPV types are divided into high-risk HPV types (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, and 58) associated with cervical cancers, and low-risk types (6, 11, 40, 42, 43, 44, and 54) associated with genital warts [17]. The E6 and E7 oncoproteins of HPV contribute to oncogenesis by associating with the tumour suppressor proteins p53 and pRb, respectively [18]. In this report, we describe the E6 and E7 genes of 14 conventional HPV species (HPV16, 31, 33, 52, 58,51,53, 66, 18, 39, 59, 68,6, 44) in Shanghai women with cervical lesions. This work provides basic information and reference variant sequences for future investigation of viral-host evolution and viral pathogenesis.
In this study, the α-9 (HPV16, 31, 33, 52, 58), α-5 (HPV51), α-6 (HPV53, 66), α-7 (HPV18, 39, 59, 68) and α-10 (HPV6, 44) were were detected and analyzed. 79.26% of α-9 HPV infection caused CIN confirmed histopathologically, 55.49% of which were HSIL. HPV16 A4, HPV31 A2, HPV33 A1, HPV52 B and HPV58 A1 were the most common sublineages in the α-9 HPV group. In China, the A1-A3 sublineage of HPV16 was predominant in northeast China [19], and A4 was common in central and south China [20, 21]. Globally, the risk of cervical cancer caused by the A3, A4 and D sublineages was significantly higher compared with HPV16 A1 [22]. In our study, HPV 31/33/52/58 had variant lineages similar to those reported by previous studies, and sublineages associated with CIN and/or cervical cancer were HPV52 C and HPV33 A1 [8, 23–26]. We should improve the screening of cervical cancer based on HPV pathogenic sub-lineages in different regions. This also reduces the rate of colposcopy biopsy, which can reduce the burden on patients and reduce the waste of medical resources. Simple infections of HPV16 carcinogenic subtypes or low-grade lesions caused by them should be intervened as early as possible rather than just follow-up. However, the sample size should be expanded to further confirm our research results.
The genome variations in humans and HPV may influence any stage of HPV infection by inducing cervical cancer [27]. For E6, the T7220G (D32E) variation in HPV16 E6 was a risk factor that increased the incidence of HSIL, whereas A388C(K93 N) variation in HPV58 E6 significantly reduced the risk of HSIL. Previous studies have shown that the susceptibility to cervical disease is increased by the specific protein interaction HPV16 E6 (L83 V)-p53 (Arg-72, [28]. Moreover, the gene variant T350G of HPV-16 was found to display more efficient degradation of Bax and binding to the E6 binding protein [29]. We found that E7 was highly conserved in the HSIL group compared to the <HSIL group, and A7689G (N29S) in E7 significantly increased the risk of HSIL. While the HPV16 A4 sublineage (P < 0.0001) and HPV16 E7 29S (P = 0.0002) rarely occurred in cancer patients compared to women with cervicitis in Vietnam [30]. HPV16 E7 S63F was significantly different between the case and control groups (P = 4.861 × 10− 10) in a Han Chinese population [31]. The T20I/G63S substitutions in HPV16 A3 E7 significantly increased the risk for HSIL in Taizhou area, China [32]. In one word, HPV sub-lineage and variation dispersal was population-specific, and we should develop different screening and treatment schemes according to the distribution of HPV variation in different regions. Due to the limitation of sample capacity, we should increase the sample size to confirm the role and mechanism of these mutations in the development of cervical cancer in Shanghai area or south China.
In current study, the E7 gene had significantly fewer nonsynonymous variants in the HSIL compared to LSIL and IF groups (P = 3.17× 10–4). Lisa Mirabello et al. confirmed hypovariation in that E7 had significantly fewer, rare non-silent genetic variants in cancers (P = 6.13× 10− 5) compared to E6 [33]. Previous studies have reported that the HPV16 E7 protein leading to cervical cancer is virtually invariant, and E7 displayed a fully conserved sequence [34, 35]. In summary, E7 variation greatly decreases the risk of CIN and invasive cancer.
Conclusions
In this study, we focused on the phylogeny and polymorphism of 14 HPV variants based on the E6 and E7 genes. In addition, we also found that the E7 gene lacked significant genetic variation in CIN, and which was strict conservation in the HSIL. This comprehensive analysis will help us understand the clinical and biological effects of sequence changes and provide preventative/therapeutic interventions for HPV-related CIN and cervical cancer.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1 Table S1. Co-variations analysis of α-9 HPV E6 and E7 gene in the case and control groups.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the American Journal Experts for English language editing.
Abbreviations
- CIN
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
- HPV
Human papillomavirus
- HSIL
High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
- LSIL
Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
Authors’ contributions
JWZ, YTR, QZY, ML and JHG conceived the study. FL and LFH directed the study. JHG and QZ contributed to the collection of samples and clinical information. YTR and ML performed PCR. JWZ performed the statistical analysis. JWZ, ML and TLZ performed the phylogenetic tree analysis and sequence analysis. JWZ, YTR, QZY, ML, JHG and TLZ wrote the manuscript with the assistance and final approval of all authors. LFH and FL corrected the manuscript. All the authors performed a critical revision of this manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant NO. 81771529, 81572546, 81972422), the Shanghai Science and Technology Development Foundation (Grant NO. 17441902500), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (NO.22120190241, 22120190214), and the Shanghai Hospital Development Center Foundation (Grant NO. 16CR3089B).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approval by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Shanghai First Maternity and Infant Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine (No: KS 1714). Informed consent was obtained from the studied patients.
Consent for publication
Informed consent Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Lingfei Han, Email: lingfeihan@126.com.
Fang Li, Email: fang_li@tongji.edu.cn.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s13027-019-0250-9.
References
- 1.Sichero L, El-Zein M, Nunes EM, Ferreira S, Franco EL, Villa LL, Ludwig-McGill Cohort S. Cervical infection with cutaneous Beta and Mucosal alpha papillomaviruses. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2017;26:1312–1320. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-0081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen Z, Schiffman M, Herrero R, DeSalle R, Anastos K, Segondy M, Sahasrabuddhe VV, Gravitt PE, Hsing AW, Chan PKS, Burk RD. Classification and evolution of human papillomavirus genome variants: Alpha-5 (HPV26, 51, 69, 82), Alpha-6 (HPV30, 53, 56, 66), Alpha-11 (HPV34, 73), Alpha-13 (HPV54) and Alpha-3 (HPV61) Virology. 2018;516:86–101. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.de Martel C, Plummer M, Vignat J, Franceschi S. Worldwide burden of cancer attributable to HPV by site, country and HPV type. Int J Cancer. 2017;141:664–670. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schiffman M, Doorbar J, Wentzensen N, de Sanjose S, Fakhry C, Monk BJ, Stanley MA, Franceschi S. Carcinogenic human papillomavirus infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16086. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cornet I, Gheit T, Iannacone MR, Vignat J, Sylla BS, Del Mistro A, Franceschi S, Tommasino M, Clifford GM. HPV16 genetic variation and the development of cervical cancer worldwide. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:240–244. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Freitas LB, Chen Z, Muqui EF, Boldrini NA, Miranda AE, Spano LC, Burk RD. Human papillomavirus 16 non-European variants are preferentially associated with high-grade cervical lesions. PLoS One. 2014;9:e100746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mirabello Lisa, Yeager Meredith, Cullen Michael, Boland Joseph F., Chen Zigui, Wentzensen Nicolas, Zhang Xijun, Yu Kai, Yang Qi, Mitchell Jason, Roberson David, Bass Sara, Xiao Yanzi, Burdett Laurie, Raine-Bennett Tina, Lorey Thomas, Castle Philip E., Burk Robert D., Schiffman Mark. HPV16 Sublineage Associations With Histology-Specific Cancer Risk Using HPV Whole-Genome Sequences in 3200 Women. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2016;108(9):djw100. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djw100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chang YJ, Chen HC, Lee BH, You SL, Lin CY, Pan MH, Chou YC, Hsieh CY, Chen YM, Cheng YJ, et al. Unique variants of human papillomavirus genotypes 52 and 58 and risk of cervical neoplasia. Int J Cancer. 2011;129:965–973. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen Z, Jing Y, Wen Q, Ding X, Wang T, Mu X, Chenzhang Y, Cao M. E6 and E7 gene polymorphisms in human papillomavirus Types-58 and 33 identified in Southwest China. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0171140. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Eckhardt M, Zhang W, Gross AM, Von Dollen J, Johnson JR, Franks-Skiba KE, Swaney DL, Johnson TL, Jang GM, Shah PS, et al. Multiple routes to Oncogenesis are promoted by the human papillomavirus-host protein network. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:1474–1489. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Estevao D, Costa NR, Gil da Costa RM, Medeiros R. Hallmarks of HPV carcinogenesis: the role of E6, E7 and E5 oncoproteins in cellular malignancy. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 1862;2019:153–162. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33:1870–1874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhang H, Gao S, Lercher MJ, Hu S, Chen WH. EvolView, an online tool for visualizing, annotating and managing phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:W569–W572. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.He Z, Zhang H, Gao S, Lercher MJ, Chen WH, Hu S. Evolview v2: an online visualization and management tool for customized and annotated phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:W236–W241. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A. G*power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods. 2007;39:175–191. doi: 10.3758/BF03193146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bergengren L, Lillsunde-Larsson G, Helenius G, Karlsson MG. HPV-based screening for cervical cancer among women 55-59 years of age. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0217108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mirbahari SG, Sadeghi M. The prevalence of genus alpha human papillomavirus in women with uterine cervical infection and/or inflammation in Western Iran. Mater Sociomed. 2018;30:113–117. doi: 10.5455/msm.2018.30.113-117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gao R, Wu X, Huang Z, Wang B, Li F, Xu H, Ran L. Anti-tumor effect of aloe-emodin on cervical cancer cells was associated with human papillomavirus E6/E7 and glucose metabolism. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:3713–3721. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S182405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhe X, Xin H, Pan Z, Jin F, Zheng W, Li H, Li D, Cao D, Li Y, Zhang C, et al. Genetic variations in E6, E7 and the long control region of human papillomavirus type 16 among patients with cervical lesions in Xinjiang, China. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:65. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0774-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cao M, Chenzhang Y, Ding X, Zhang Y, Jing Y, Chen Z. Genetic variability and lineage phylogeny of human papillomavirus type-16 and -53 based on the E6, E7, and L1 genes in Southwest China. Gene. 2016;592:49–59. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.07.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liu Y, Pan Y, Gao W, Ke Y, Lu Z. Whole-genome analysis of human papillomavirus types 16, 18, and 58 isolated from cervical Precancer and Cancer samples in Chinese women. Sci Rep. 2017;7:263. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00364-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Clifford GM, Tenet V, Georges D, Alemany L, Pavon MA, Chen Z, Yeager M, Cullen M, Boland JF, Bass S, et al. Human papillomavirus 16 sub-lineage dispersal and cervical cancer risk worldwide: whole viral genome sequences from 7116 HPV16-positive women. Papillomavirus Res. 2019;7:67–74. doi: 10.1016/j.pvr.2019.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang J, Zhang S, Wang M, Ding X, Wen Q, Chen Z, Cao M, Jing Y, Zhang S. Genetic variability in E5, E6, E7 and L1 genes of human papillomavirus type 31. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17:5498–5507. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ferenczi A, Gyongyosi E, Szalmas A, Laszlo B, Konya J, Veress G. Phylogenetic and functional analysis of sequence variation of human papillomavirus type 31 E6 and E7 oncoproteins. Infect Genet Evol. 2016;43:94–100. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.05.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tenjimbayashi Y, Onuki M, Hirose Y, Mori S, Ishii Y, Takeuchi T, Tasaka N, Satoh T, Morisada T, Iwata T, et al. Whole-genome analysis of human papillomavirus genotypes 52 and 58 isolated from Japanese women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive cervical cancer. Infect Agent Cancer. 2017;12:44. doi: 10.1186/s13027-017-0155-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chen AA, Heideman DA, Boon D, Chen Z, Burk RD, De Vuyst H, Gheit T, Snijders PJ, Tommasino M, Franceschi S, Clifford GM. Human papillomavirus 33 worldwide genetic variation and associated risk of cervical cancer. Virology. 2014;448:356–362. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.10.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schiffman M, Wentzensen N. Human papillomavirus infection and the multistage carcinogenesis of cervical cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2013;22:553–560. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Moschonas George D., Tsakogiannis Dimitris, Lamprou Konstantinos A., Mastora Eirini, Dimitriou Tilemachos G., Kyriakopoulou Zaharoula, Kottaridi Christine, Karakitsos Petros, Markoulatos Panayotis. Association of codon 72 polymorphism of p53 with the severity of cervical dysplasia, E6-T350G and HPV16 variant lineages in HPV16-infected women. Journal of Medical Microbiology. 2017;66(9):1358–1365. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lichtig H, Algrisi M, Botzer LE, Abadi T, Verbitzky Y, Jackman A, Tommasino M, Zehbe I, Sherman L. HPV16 E6 natural variants exhibit different activities in functional assays relevant to the carcinogenic potential of E6. Virology. 2006;350:216–227. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.01.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pham TTT, Bi X, Hoang HTT, Ishizaki A, Nguyen MTP, Nguyen CH, Nguyen HP, Pham TV, Ichimura H. Human papillomavirus genotypes and HPV16 E6/E7 variants among patients with genital cancers in Vietnam. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2018;71:419–426. doi: 10.7883/yoken.JJID.2018.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhou Z, Yang H, Yang L, Yao Y, Dai S, Shi L, Li C, Yang L, Yan Z, Yao Y. Human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 gene variations associated with cervical cancer in a Han Chinese population. Infect Genet Evol. 2019;73:13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yu JH, Shi WW, Zhou MY, Liu JM, Han QY, Xu HH. Genetic variability and oncogenic risk association of human papillomavirus type 58 E6 and E7 genes in Taizhou area, China. Gene. 2019;686:171–176. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.11.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mirabello L, Yeager M, Yu K, Clifford GM, Xiao Y, Zhu B, Cullen M, Boland JF, Wentzensen N, Nelson CW, et al. HPV16 E7 genetic conservation is critical to carcinogenesis. Cell. 2017;170:1164–1174. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.08.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Safaeian M, van Doorslaer K, Schiffman M, Chen Z, Rodriguez AC, Herrero R, Hildesheim A, Burk RD. Lack of heterogeneity of HPV16 E7 sequence compared with HPV31 and HPV73 may be related to its unique carcinogenic properties. Arch Virol. 2010;155:367–370. doi: 10.1007/s00705-009-0579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Roman A, Munger K. The papillomavirus E7 proteins. Virology. 2013;445:138–168. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.04.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1 Table S1. Co-variations analysis of α-9 HPV E6 and E7 gene in the case and control groups.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.