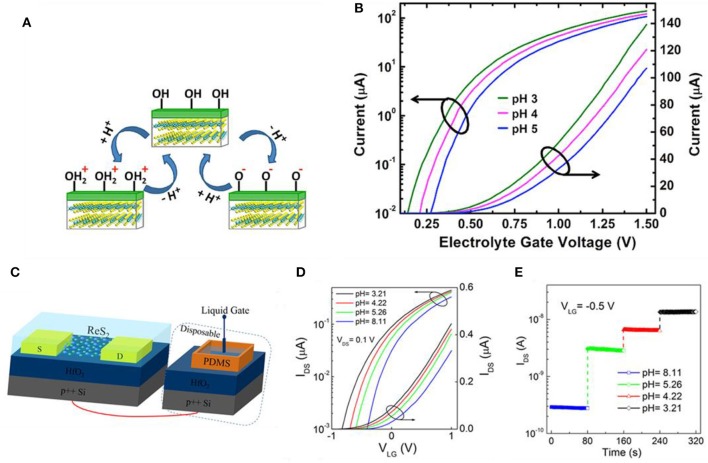
Figure 4.
MoS2 FET and ReS2 FET pH sensors. (A) Sensing mechanism of MoS2 pH sensors. At low pH, forms by protonation of OH on the dielectric surface, consequently forming a positive surface charge on the dielectric. At high pH, O− forms by deprotonation of OH on the dielectric surface, consequently forming a negative surface charge on the dielectric. (B) Drain current vs. electrolyte gate voltage in various pH values for an n-type MoS2 FET. Figures (A,B) were reproduced from Sarkar et al. (2014) with permission from the American Chemical Society. (C) Illustration of ReS2 FET for pH sensing. (D) Transfer curves (IDS-VLG) at various pH values. (E) Response curves at different pH with VDS = 0.1 V and VLG = −0.5 V at RT. Figures (C–E) were reproduced from Liao et al. (2018) with permission from the American Chemical Society.