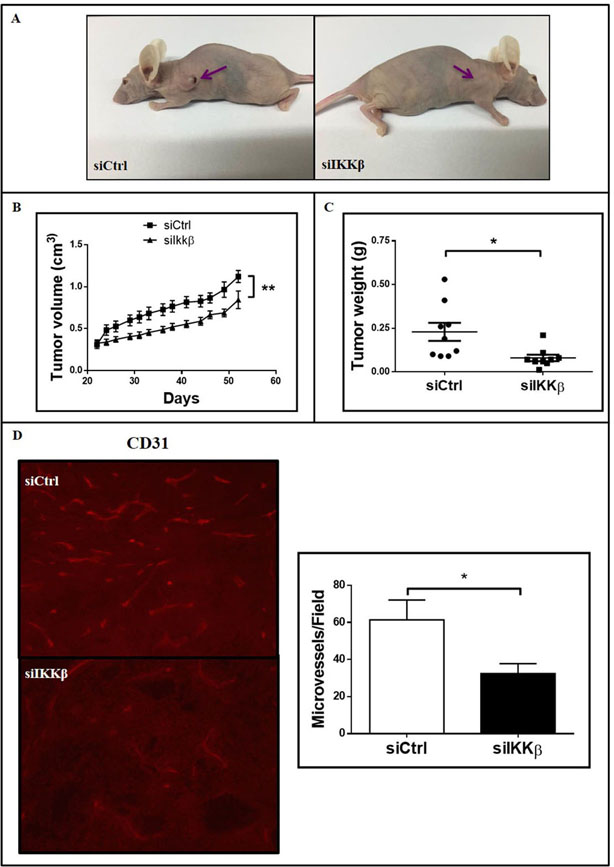
Figure 3. siRNA-mediated inhibition of IKKβ expression decreases tumor growth and angiogenesis in vivo.
1 × 106 A549 cells transfected with a non-targeting control siRNA (siCtrl) or with a siRNA smartpool targeting IKKβ (siIKKβ) were injected subcutaneously into flanks of nude mice (n=9 per group). (a) Representative images of tumor-bearing nude mice 55 days after inoculation. (b) Tumor growth kinetics assessed by tumor volume measurements overtime as indicated. Each point represents average ± 1s.d. of each group. (c) Dot plot representing individual tumor weights 55 days after inoculation. Horizontal bars represent average weight in each group. (d) IKKβ expression was evaluated in tumor sections by immunostaining as described in methods. Right) Representative images of stained tumor sections. Left) Quantitation of IKKβ-staining intensity (right). (e) Vessel density was evaluated in tumor sections by immunofluorescence staining for CD31 as described in methods. Left) Representative images of stained tumor sections. Right) Quantitation of CD31-stained vessels. Statistical significance was determined by the Student’s t-test (*p<0.05) and the significantly different comparisons are indicated by vertical (b) or horizontal (c, d) bars. Error bars represent average ± 1s.d.