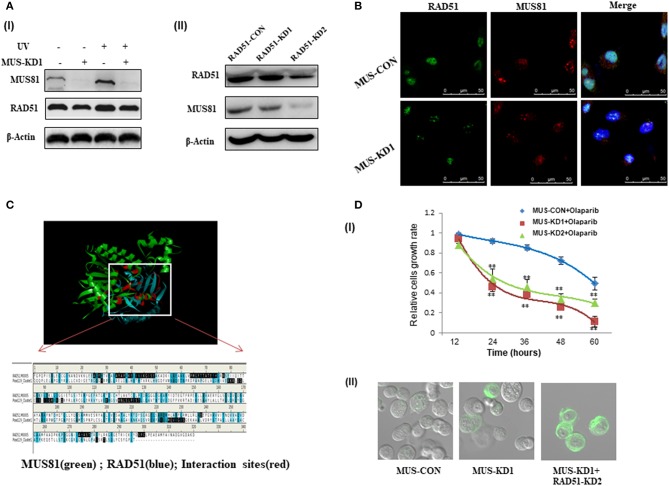
Figure 4.
The interaction between MUS81 and RAD51 influenced SOC (SKOV3 and HO8910) cells' sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents. (A) The association of MUS81 and RAD51 expression was evaluated. (I) Silencing MUS81 resulted in the decreased expression of RAD51, and both MUS81 and RAD51 were upregulated after UV exposure. (II) RAD51 knockdown was accompanied by downregulation of MUS81. (B) The co-localization of MUS81 and RAD51 was observed by immunofluorescence detection. MUS81 was co-localized with RAD51 in the nuclei. (C) The potential interaction between MUS81 and RAD51 was analyzed by Discover Studio. (D) MUS81 suppression was involved in SOC cells sensitivity to DNA damage. (I) MUS81 knockdown enhanced SOC cells sensitivity to the DNA-damaging agent Olaparib (**P < 0.01). (II) Simultaneous suppression of MUS81 and RAD51 in the transduced SOC cells was associated with around 70% of cells undergoing apoptosis, whereas 30–40% of MUS-KD cells and only 5% of MUS-CON had evidence of apoptosis. Apoptosis was detected by evaluating the ability of cells to bind lactadherin, which interacts with phosphatidylserine exposed during apoptosis.