Figure 1.
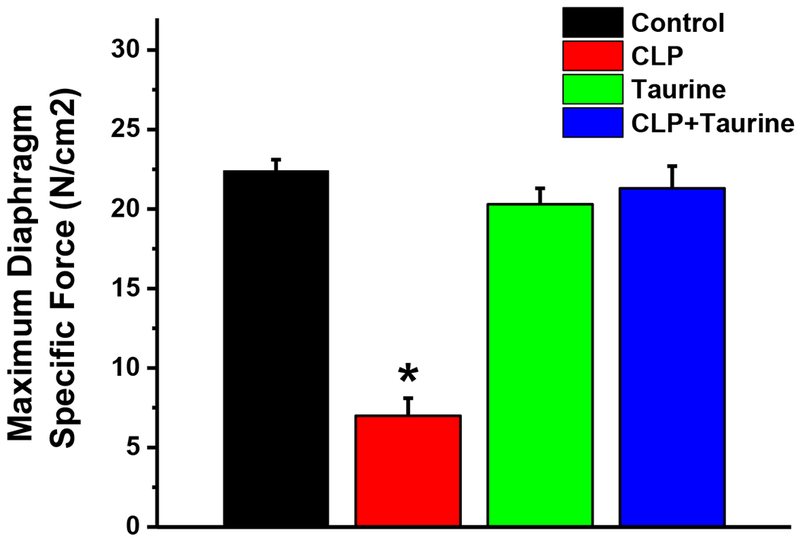
Maximum diaphragm specific force generation in (a) sham operated controls (black), (b) cecal ligation puncture (CLP, red), (c) sham operated + taurine (Taurine, green); and (d) CLP + taurine treated animals (blue). Data represents group mean average ± 1 SEM. Maximum specific force was significantly lower for the CLP group compared to the control group (p<0.001). Taurine treatment prevented CLP induced reductions in force, with maximum force for the CLP + taurine group similar to the control group and significantly higher than the CLP group (p<0.001). Maximum force for the sham + taurine group was similar to controls. * indicates statistical significance.
