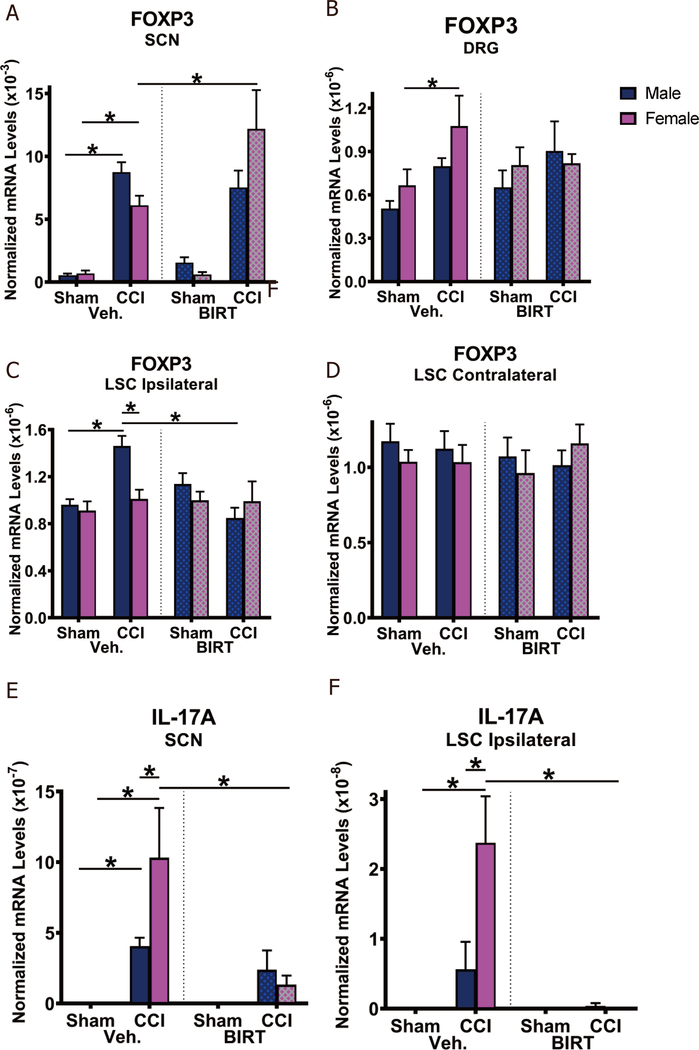
Figure 4.
Sex differences in anti-inflammatory FOXP3 and proinflammatory IL-17A from damaged sciatic nerve and in spinal cord. Tissues were collected from behaviorally verified mice as represented in Figure 2B. (A) From ipsilateral sciatic nerve (SCN), CCI induced a significant increase in FOXP3 mRNA expression (F1,1 = 76.18, P < 0.0001), with CCI-treated females responding to BIRT377 treatment to a greater degree than males (F1,1 = 5.38, P = 0.025). (B) In the ipsilateral DRGs, FOXP3 mRNA levels were elevated following CCI (F1,1 = 6.55, P = 0.014), post hoc comparisons revealed significant increases in FOXP3 mRNA levels in females with CCI compared to the sham controls. (C) In the ipsilateral lumbar spinal cord (LSC) dorsal horn, post-CCI induction in FOXP3 mRNA levels was observed in males (P = 0.0006). Following CCI, males displayed significantly greater FOXP3 mRNA levels than in females (P = 0.001). BIRT377 treatment reduced FOXP3 in males with CCI (P < 0.0001), a significant interaction between surgery, injection, and sex (F1,1 = 6.5, P = 0.014) was observed. (D) In the contralateral dorsal horn, FOXP3 levels were comparable between groups. (E) Post-CCI IL-17A mRNA levels were significantly elevated at the ipsilateral sciatic nerve (F1,1 = 21.93, P < 0.0001). BIRT377 treatment reduced post-CCI IL-17A mRNA levels (F1,1 = 21.93, P < 0.0001), with post hoc comparisons revealing a significant reduction of IL-17A mRNA levels following BIRT377 treatment in females with CCI. (F) In the ipsilateral dorsal horn, post-CCI IL-17A mRNA levels were elevated (F1,1 = 14.85, P = 0.0004). BIRT377 treatment reduced IL-17A mRNA levels in mice with CCI (F1,1 = 14.07, P = 0.0006), which occurred in females to much a greater degree than males (F1,1 = 5.71, P = 0.02). Post-CCI induction in IL-17A mRNA levels were much greater in females, than in males (F1,1 = 5.23, P = 0.02). *p values from post hoc comparisons ranges from P = 0.04 to P < 0.0001. n = 5 in female CCI + BIRT data for DRG FOXP3.n = 6 per group unless otherwise indicated