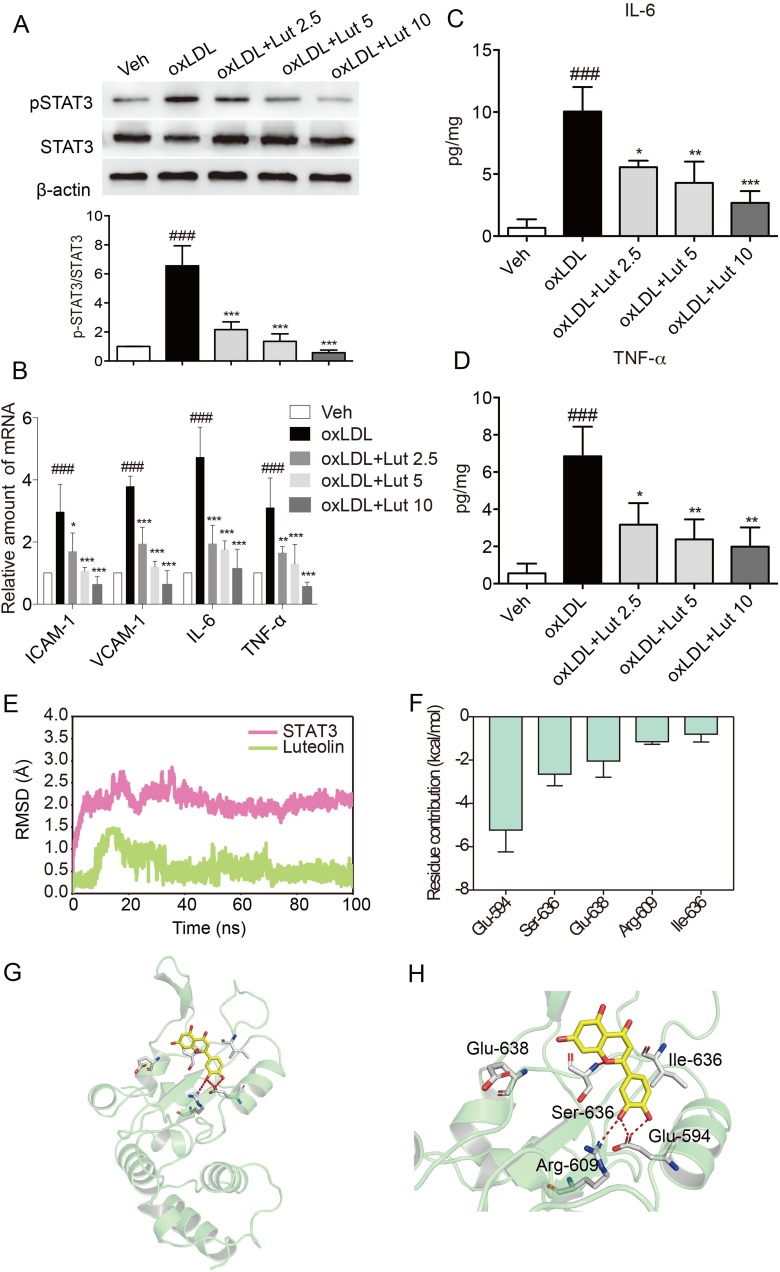
Figure 5.
Luteolin suppressed inflammation in oxLDL-stimulated macrophages.
Notes: (A) Luteolin suppressed oxLDL-induced activation of STAT3. Primary macrophages were pretreated with luteolin (Lut, 2.5, 5 or 10 μM), or vehicle (DMSO, 1 μL) for 1 hr and then stimulated with oxLDL (50 µg/mL) for 15 mins. Total proteins were extracted to detect the levels of p-STAT3 and STAT3. (B) Luteolin inhibited oxLDL-induced increase in mRNA levels of inflammatory molecules. Macrophages were pretreated with Lut (2.5, 5 or 10 μM) or vehicle (DMSO, 1 μL) for 1 hr and then stimulated with oxLDL (50 µg/mL) for 6 hrs. Figure showing mRNA levels of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, IL-6 and TNF-α. (C, D) Luteolin inhibited oxLDL-induced release of cytokines. Macrophages were pretreated with Lut (2.5, 5 or 10 μM) or vehicle (DMSO, 1 μL) for 1 hr and then stimulated with oxLDL (50 µg/mL) for 24 hrs. The levels of IL-6 (C) and TNF-α (D) in the culture medium were detected by ELISA. (E) RMSD curves for the 100 ns molecular dynamics simulation. (F) Top 5 contributing residues of STAT3 SH2 domain to luteolin binding. (G) Overview of contributed residues of STAT3 SH2 domain to luteolin binding. (H) Detailed view of STAT3 SH2 domain to Luteolin binding. (n=3 in each group; ###P<0.001, vs vehicle group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P< 0.001, vs oxLDL group).