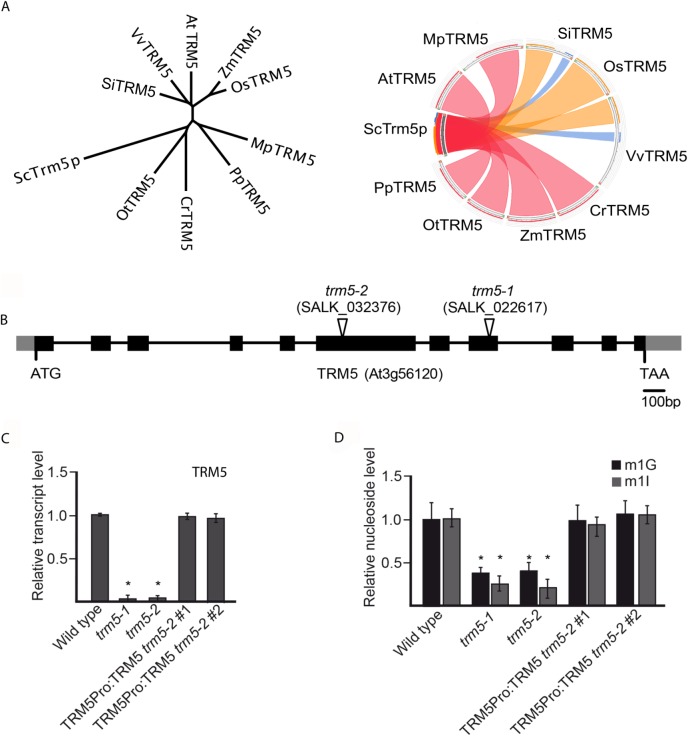
Fig 1. TRM5 is conserved in plants and has dual-functionality in modifying RNA bases.
(A) Unrooted phylogenetic tree and sequence conservation Circos plot of putative TRM5 proteins from yeast (Sc), tomato (Sl), grape (Vv), Arabidopsis (At), maize (Zm), rice (Os), Marchantia (Mp), Physcomitrella (Pp), Chlamydomonas (Cr), and Ostreococcus (Ot). The ribbons were coloured based on sequence identity, with blue < = 25%, green 25–50%, orange 51–75% and red for 76–99%. (B) Exon-intron structure of the putative TRM5 locus (At3g56120) showing the T-DNA insertion sites of the trm5-1 and trm5-2 alleles (as indicated by the open triangles). Black boxes and grey boxes represent coding regions and untranslated regions, respectively. (C) Relative transcript level detected by qPCR in wild type, trm5-1 or trm5-2 seedlings. (D) Relative nucleoside level of modification m1G and m1I detected by HPLC/MS in wild type, trm5-1 or trm5-2 seedlings.