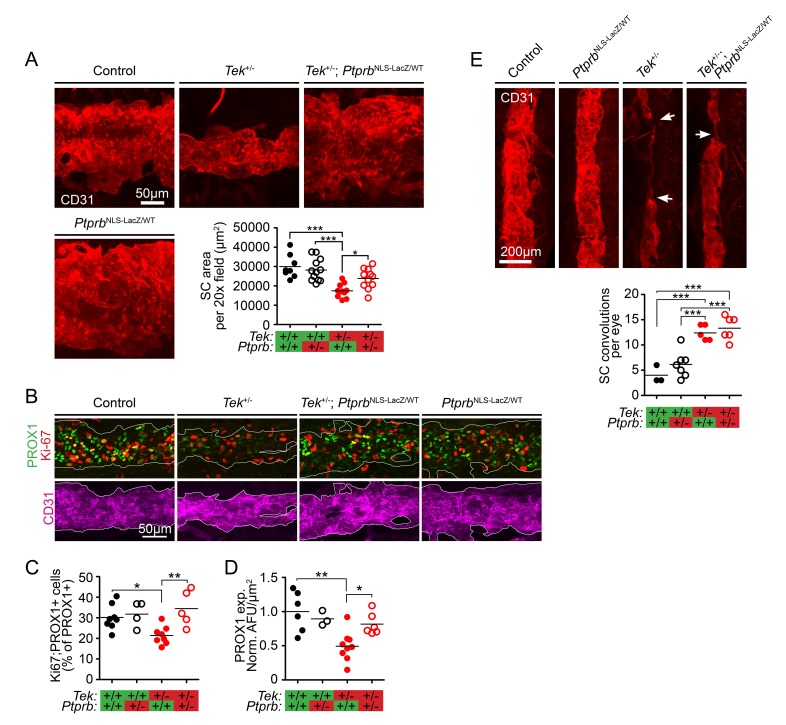
Figure 2. TEK signaling has a dose-dependent effect on Schlemm’s canal (SC) area and development.
(A) Confocal microscopy of whole mount eyes revealed reduced CD31+ SC area in adult Tek+/- haploinsufficient mice. This phenotype was blunted in Tek+/-;PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT double heterozygous animals, confirming the importance of TEK activation in canal development. PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT heterozygous controls had normal SC area (n = 8 WT, 12 PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT, 11 Tek+/- and 11 Tek+/-;PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT mice). 20x fields shown represent an area of 65,536 μm2. Images were captured as 10-frame Z stacks with a step size of 1.67 μm and a pinhole of 1.2 Airy units, and are shown as maximum intensity projections. (B, quantified in C) At postnatal day 5 (P5), confocal microscopy of the developing SC in eye whole mounts revealed reduced numbers of proliferating Ki-67-positive SC ECs (Ki67-PROX1 double positive cells) in Tek haploinsufficient animals compared to littermate WT or PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT controls. Normal proliferation was observed in Tek+/-;PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT animals. (D) Compared to control and PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT mice, PROX1 expression was reduced in Tek+/- littermate eyes. Expression was normal in Tek+/-;PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT double heterozygotes. n = 8 (WT), 4 (PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT), 8 (Tek+/-) and 5 (Tek+/-;PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT) Shown are maximum intensity projections from 8-frame confocal Z stacks captured using a 20x objective, step size of 1 μm and pinhole of 1.2 Airy units. Norm. AFU: Normalized, background subtracted arbitrary fluorescence units. (E) Compared to control and PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT littermates, confocal analysis of adult SC revealed a marked increase in the number of focal convolutions and narrowings in the eyes of Tek+/- and Tek+/-;PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT mice. N = 4 (WT), 7 (PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT), 5 (Tek+/-) and 6 (Tek+/-;PtprbNLS-LacZ/WT). Horizontal lines indicate population means. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 as determined by 1-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s correction.