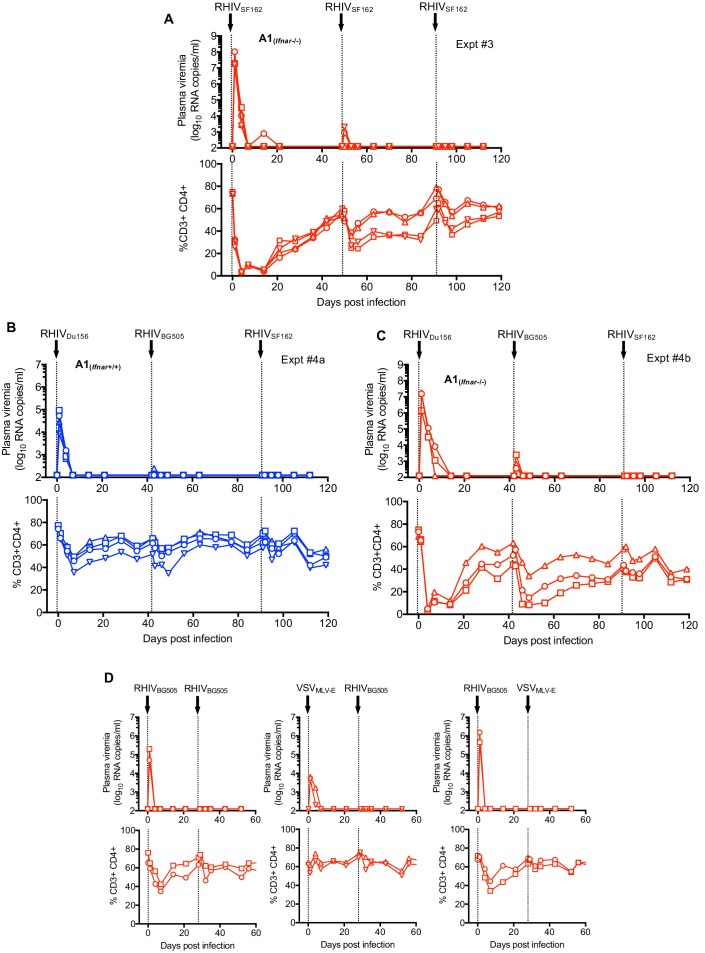
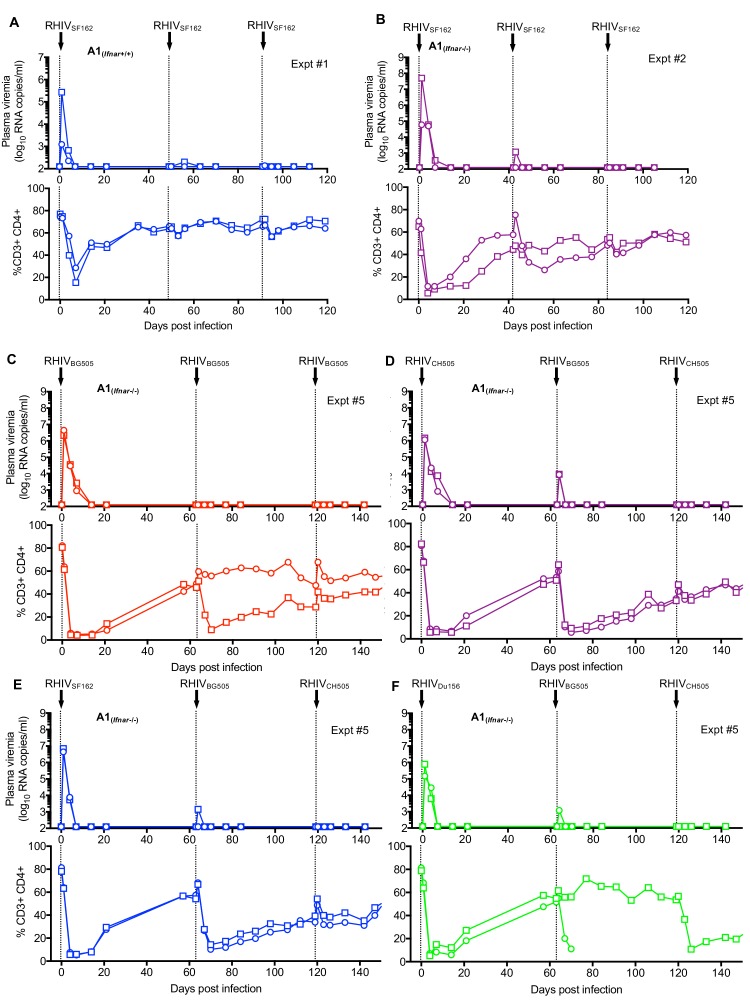
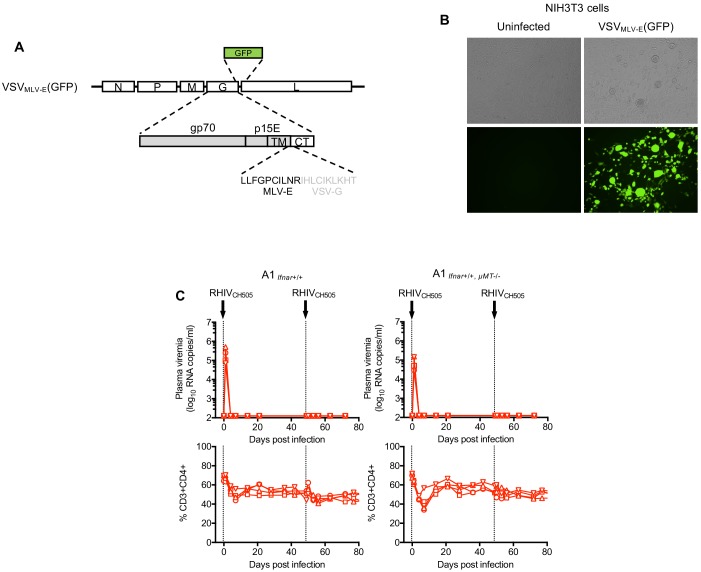
Figure 6. Protection against RhIV reinfection.
(A) RhIV viremia (log10 RNA copies/ml of plasma, upper rows) and blood CD4+ T-cell proportion (% of CD3+ cells, lower rows) in A1Ifnar-/- mice following infection with RhIVSF162 on days 0, 49 and 91. Each symbol type represents an individual mouse (n = 4). (B, C) RhIV viremia (log10 RNA copies/ml of plasma, upper rows) and blood CD4+ T-cell proportion (% of CD3+ cells, lower rows) in A1Ifnar+/+ mice (B) and A1Ifnar-/- mice (C) following infection with RhIVDu156, RhIVBG505, and RhIVSF162 on days, 0, 42 and 91, respectively. Each symbol type represents an individual mouse (n = 4). (D) RhIVBG505 and VSVMLV-E viremia (log10 RNA copies/ml of plasma, upper rows) and blood CD4+ T-cell proportion (% of CD3+ cells, lower rows) in A1Ifnar-/- mice following infection with RhIVBG505 on day 0 and day 28 (left panels), VSVMLV-E on day 0 and RhIVBG505 day 28 (center panels) or RhIVBG505 on day 0 and VSVMLV-E day 28 (right panels).