Fig. 4.
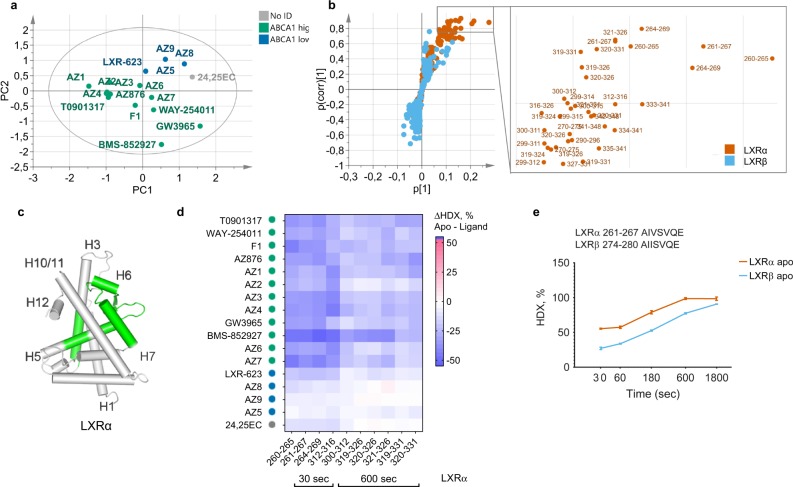
Multivariate analysis reveals structural determinants of high intestine Abca1 induction. a PCA score scatter plot of the first two principal components. Green dots: LXR ligands inducing high intestine Abca1 levels, blue dots: low inducers of ABCA1, and gray dots: compounds with no assigned ABCA1 class. R2X(cum) = 83.4%, Q2(cum) = 62.9%, n = 17. b S plot of the ABCA1 OPLS-DA and the zoomed-in part of the plot representing limits used for the selection of differential peptides with the highest contribution to class separation (|p(corr)| > 0.7, p > 0.05). Orange dots: LXRα peptides, cyan dots: LXRβ peptides. c Statistically significant (p-value < 0.05, two-tailed Student’s t test) predictive peptides better stabilized by potent ABCA1 inducers mapped on the LXRα crystal structure (2ACL.pdb). d Average differences in deuteration levels of the differential peptides having the highest correlation to the class separation (|p(corr)| > 0.8). e Time-point deuteration kinetics of the central part of H3 (LXRα peptides 261–267, orange and LXRβ peptides 274–280, cyan). HDX-MS data were collected in triplicate (±standard deviation), and deuteration data are normalized to the fully deuterated control.