Figure 8.
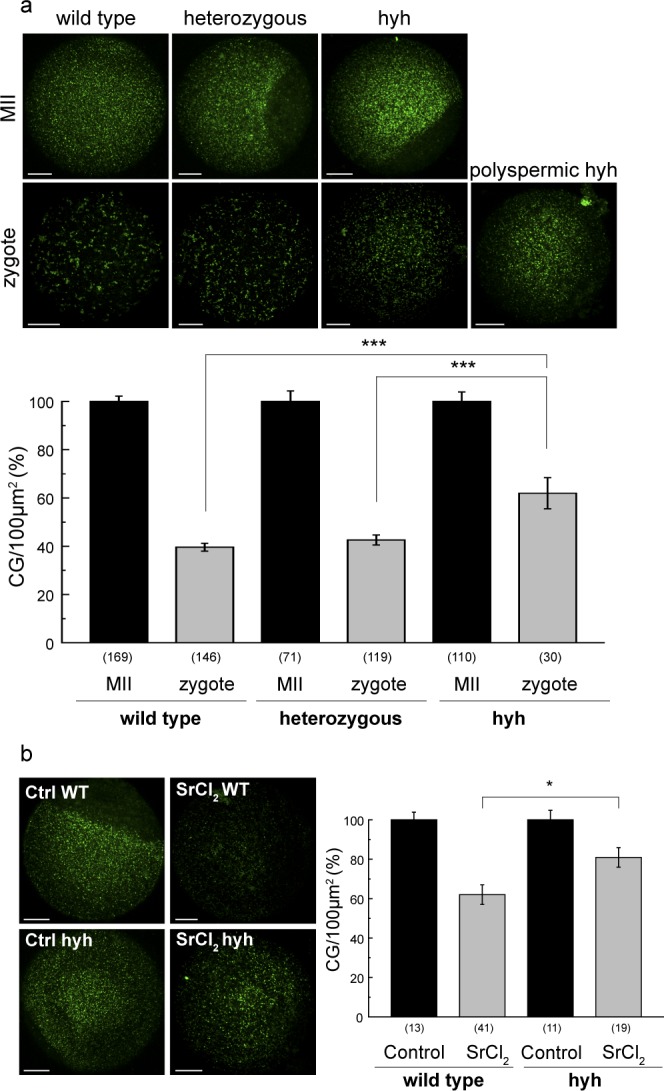
Hyh oocytes exhibit an impaired deficient cortical reaction. (a) Cortical granule exocytosis (CGE) after IVF in wild type, heterozygous and hyh oocytes.Upper panel: representative confocal images of MII oocytes and 2PN zygotes of each genotype, stained with FITC-LCA to label cortical granules. A polyspermic hyh zygote is presented to show the absence of CGE despite fertilization. Scale bar: 20 μm. Lower panel: histogram showing CG density/100 μm2 for each genotype. Data are shown as mean ± SEM from at least 4 independent experiments. Numbers in parentheses below bars represent the total number of cells analyzed; ***p ≤ 0.001 (Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons, zygotes). Zygotes vs. MII oocytes comparison in each genotype show significant CGE (***p ≤ 0.001; Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons). (b) CGE functional assay in wild type and mutant homozygous (hyh) MII oocytes. MII oocytes were subjected to CGE activation triggered with 30 mM strontium chloride (SrCl2). Left, representative confocal images of MII oocytes stained with FITC-LCA to label cortical granules. Scale bar: 20 μm. Right, histograms showing CG density/100 μm2 for each genotype. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; numbers in parentheses represent the total number of MII oocytes in each condition. *p ≤ 0.05 (Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons). Control vs. SrCl2 activated MII oocytes comparison in each genotype show significant CGE (***p ≤ 0.001; Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons).
