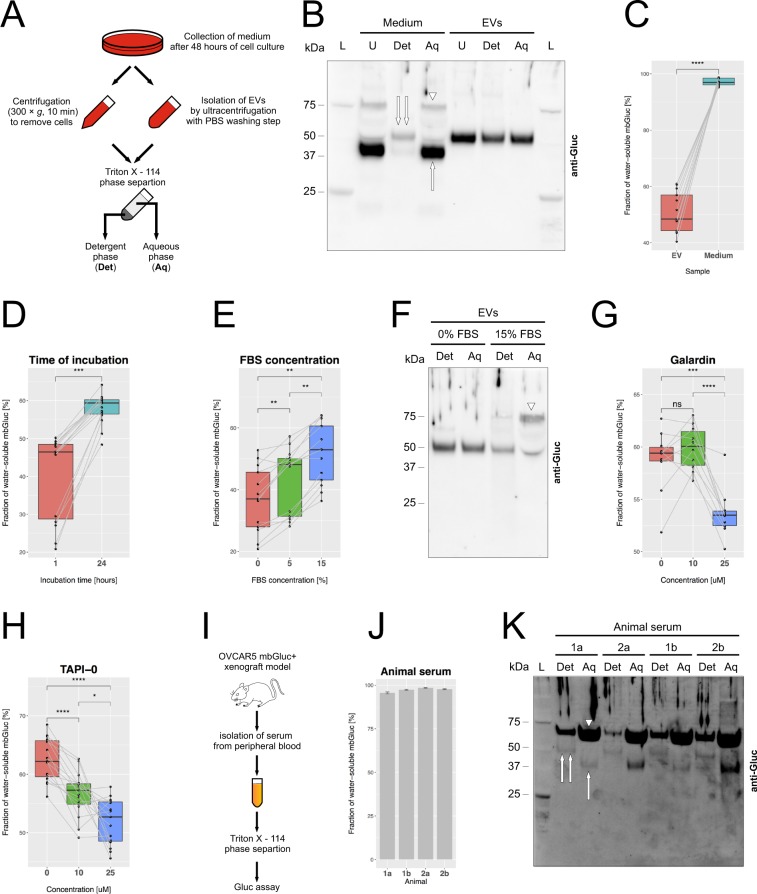
Figure 6.
mbGluc Provides a Quantitative Measure of Shedding of Proteins from EV Membranes in Vitro and in Vivo. (A) Schematic of procedure to separate water-soluble freely floating (“Aq”) from detergent-soluble with transmembrane domain (“Det”) proteins by TritonX – 114 (TX-114) method. (B) Western blot of mbGluc protein isolated from OVCAR5-mbGluc+ conditioned medium and EVs (isolated by UC) subjected to TX-114 phase separation. The water-soluble form of mbGluc (aqueous phase) was present as proteins of approximately 40 kDa (single arrow) and 80 kDa (arrowhead). In the detergent phase, mbGluc band corresponded to approximately 50 kDa, the same as detected in unprocessed EVs (compare to Fig. 3C). L – ladder, U – unprocessed sample (no TX-114 separation), Det – detergent phase of TX-114 separation, Aq – aqueous phase of TX114 separation. (C) Fraction of water-soluble mbGluc based on bioluminescence in OVCAR5-mbGluc+ conditioned medium and EVs isolated by UC. EVs were fractionated by TX-114 procedure with two separation cycles. (D) Fraction of water-soluble mbGluc in the medium (with 0% FBS) with EVs incubated for 1 and 24 hours at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator. (E) Fraction of water-soluble mbGluc in EVs incubated for 1 hour in the medium supplemented with 0, 5 and 15% FBS at 37 °C. (F) Western blot of mbGluc protein in medium with EVs incubated for 1 hour in the medium with 0 and 15% FBS subjected to TX-114 phase separation. FBS promoted the appearance of an 80 kDa protein, observed previously in the medium (arrowhead, lane “15% FBS, Aq”, compare to (B). (G) Fraction of water-soluble mbGluc in EVs incubated for 24 hours in medium supplemented with 5% FBS and a broad-spectrum MMPs inhibitor GM6001 (galardin). (H) Fraction of water-soluble mbGluc in EVs incubated for 24 hours in the medium supplemented with 5% FBS and TAPI-0, a potent inhibitor of MMPs and ADAM17. (I) Schematic of serum isolation from mice bearing OVCAR5-mbGluc+ tumors. Serum was subjected to TX-114 procedure and analyzed by Gluc assay. (J) Fraction of water-soluble mbGluc in serum from OVCAR5-mbGluc+ mice 1 and 2 (two separate serum samples “a” and “b” were analyzed from each animal, bioluminescent measurements were done in 3 technical replicates). (K) Western blot of mbGluc protein in serum from OVCAR5-mbGluc+ mice 1 and 2 (technical replicates a and b in each) separated by TX-114 method. The signal in aqueous phase was mainly coming from an 80 kDa protein (arrowhead) as well as from 40 kDa band (single arrow, lanes “Aq”). A simultaneous presence of 80 kDa and 40 kDa suggests that fragments of mbGluc may form dimers after being cleaved-off. The 50 kDa band characteristic of EV-bound mbGluc was detected in detergent phases from all serum samples (double arrow, lanes “Det”). For all experiments in B-H, EVs were isolated by two UC steps (120 K × g, 2 hours). The pellet was dissolved in RPMI medium and incubated at 37 °C under conditions specified above for 24 hours (unless specified otherwise). The medium was subsequently separated by TX-114 into water-soluble and detergent-soluble phase. Plots in C-H demonstrate data from 3 experiments, in each there were 5 technical replicates of Gluc bioluminescence.