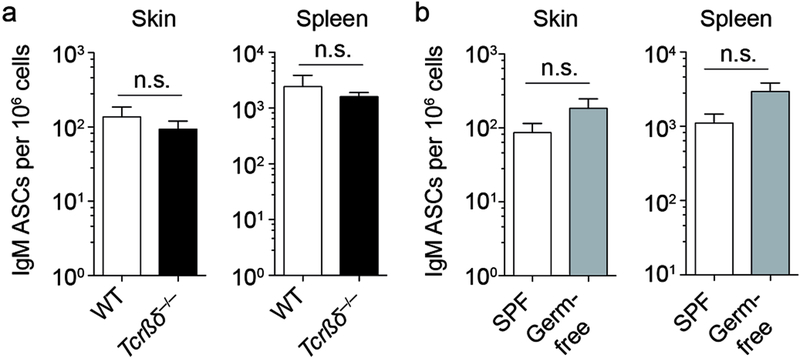
Figure 2. Skin IgM ASCs develop independently of T cells and microbial colonization.
(a and b) Skin and spleen cells were isolated from naïve mice. Frequency of IgM ASCs among all isolated cells was determined by ELISPOT assay analyzing wildtype and T cell-deficient Tcrβδ−/− mice (a) or specific pathogen free (SPF) and germ-free mice (b). Data points indicate the mean ± SEM of 15–23 mice per group from 3 independent experiments (a) or of 8–10 mice per group from 2 independent experiments (b). WT, wildtype; SPF, specific pathogen-free; n.s., not significant using the Mann Whitney test.