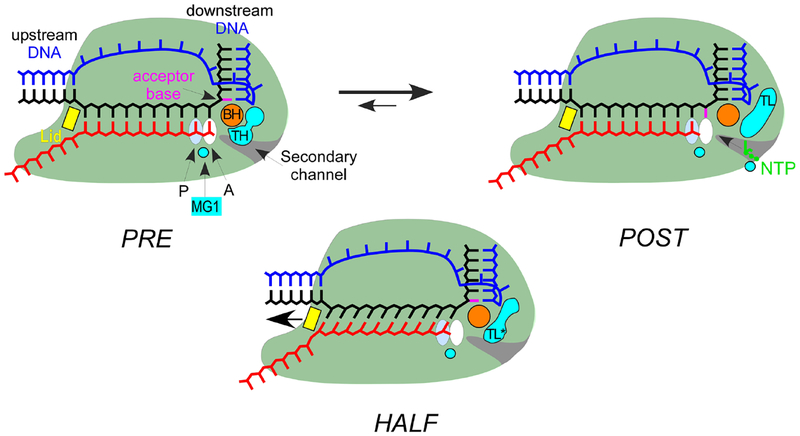
Fig. 5.
Schematics of half and complete translocations. In the pre-translocated TEC (left), the 3’ hydroxyl is bound in the A-site and the TL is folded into TH, forming the THB. Translocation by one nt generates the post-translocated TEC (right) in which the 3’ OH is bound in the P-site, the tDNA acceptor base (magenta) is positioned in the A-site to pair with the incoming NTP substrate, and the TL is unfolded. In some TECs structures, RNA is fully translocated but tDNA translocates only partially [146] or not at all [37]; in both cases, the acceptor base has not moved to the A-site, blocking substrate binding (center). The tDNA The asynchronous translocation lengthens the RNA:DNA hybrid and changes its tilt, necessitating shifting the β’ lid (yellow) and possibly stabilizing an altered state of the TL (TL*).