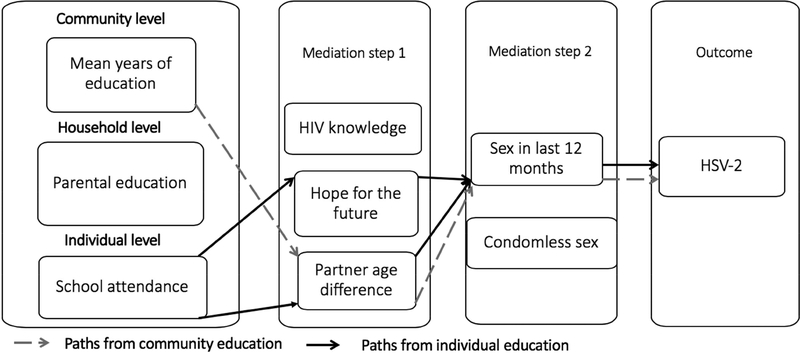
Figure 2: Significant pathways for the effect of multilevel measures of schooling on incident HSV-2 infection*.
*All paths were significant at alpha <.05; Path for mean community level of education (B: .03; 95% CI .01–.05);
Path for school attendance through future aspirations (B: .00; 95% CI .00–.01); Path for school attendance through partner age (B: .05; 95% CI .02–.09); N=6,723 person-time observations from 1,691 participants.
*Definitions: Low school attendance <80% of school days, age-disparate relationship (partner aged ≥5 years), low HIV knowledge (≤50% correct); Community mean years of education. HSV-2, Herpes simplex virus type 2