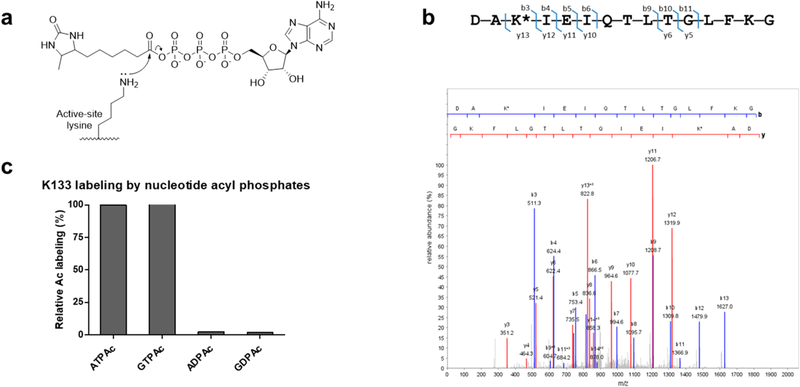
Figure 1.
Chemoproteomic identification of the acylated K133 peptide from procaspase-6. (a) ATPAc (Ac = desthiobiotinyl) along with the corresponding ADPAc, GTPAc, and GDPAc probes used in this study. Desthiobiotin shows superior properties for capture by and release from streptavidin beads compared to those of biotin on our chemoproteomic platform. For a full description of the platform, see Methods and Figure S1.(b) Identification of the acylated K133 peptide by LC–MS/MS spectra from a proteomic lysate of Jurkat cells treated with ATPAc. Peaks including the site of acylation (asterisk) are matched in agreement with a high cross-correlation score (Xcorr > 5.0). Translation of amino acid sequence using genomic database sequences confirmed the peptide was derived from CASP6. (c) Relative amounts of streptavidin-captured, acylated K133 peptide determined by LC–MS/MS using four related acyl phosphate probes. Percents are based on ATPAc capture defined as 100% under these experimental conditions.