Figure 3.
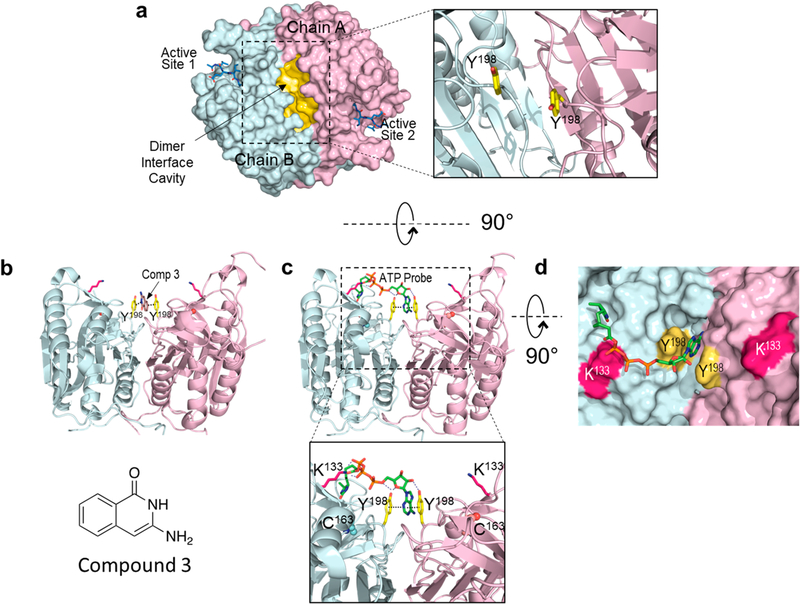
Structural models of the ATP binding site at the dimer interface of procaspase-6. (a) Structure of the procaspase-6 dimer highlighting the hydrophobic cavity (yellow) at the dimer interface. This cavity is observed in the executioner caspase-3, −6, and −712,13 as well as caspase-1.11,12 Tyrosine 198 (yellow sticks) has been identified as a site that is critical for ATP binding (inset). (b) The adenine ring in the acyl phosphate probe (green sticks) is predicted to bind between the two Y198 residues at the dimer interface. This allows covalent modification of K133, which is located at the edge of the cavity ~18 Å from the adenine-Y198 pair. (c) The crystal structure of compound 3 (brown sticks), identified by SPR as a caspase-6 inhibitor, can be similarly observed sandwiched between the Y198 (yellow) pair of the procaspase-6 dimer.13 (d) The modeled interaction between the acyl phosphate probe and procaspase-6 shows excellent shape complementarity.