Figure 2.
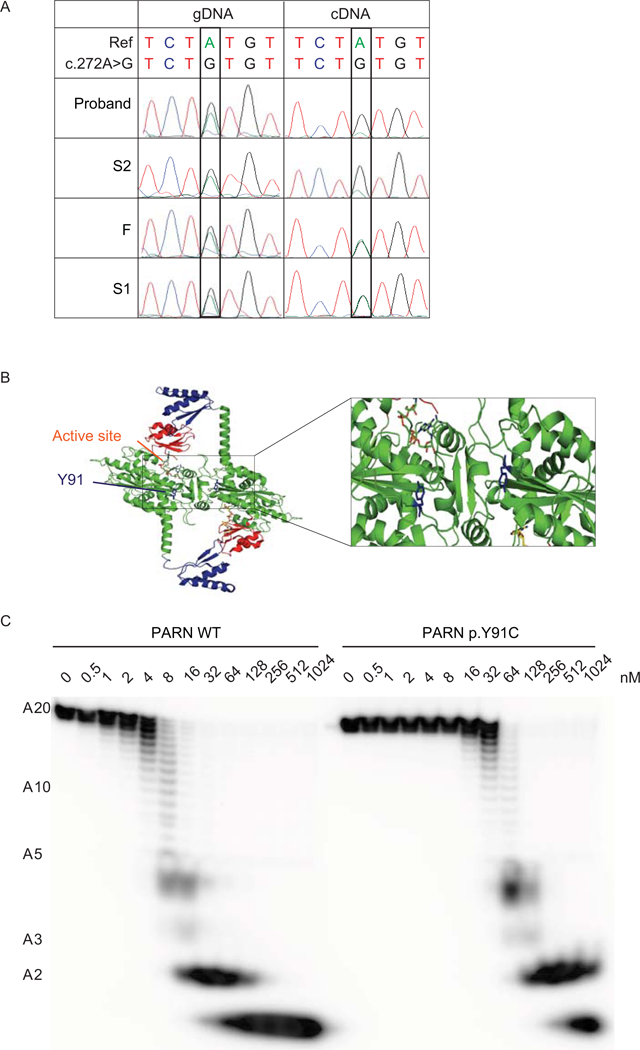
The PARN variant transcript encoding p.(I274*) is subject to NMD and the PARN p.Y91C mutant protein has decreased deadenylation activity. (A) Sanger sequencing of gDNA and cDNA from peripheral blood from the indicated individuals in the region encompassing NM_002582.3: c.272A; p.Y91. (B) Localization of residue Y91 (blue) in the dimeric model of PARN (Virtanen et al., 2013), based on crystal structures PDB: 2A1R (Wu et al., 2005), 2A1S (Wu et al., 2005) and 3D45 (Wu et al., 2009). The expanded view highlights the location of residue Y91 near the active site and the dimer interface in each monomeric subunit of PARN. (C) Deadenylation activity of PARN WT or p.Y91C using the indicated concentrations of recombinant protein expressed and a 5’ end-labeled A20 homopolymeric RNA substrate.
