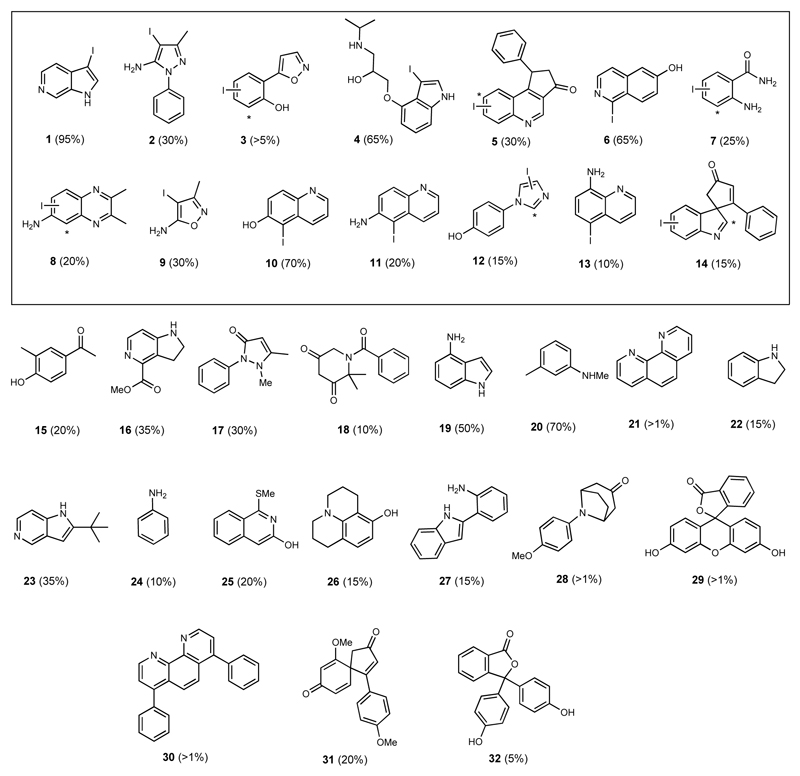
Fig. 2. Diverse substrate scope of VirX1.
Biocatalytic halogenation using VirX1 of a 400-member compound library revealed 32 compounds as being accepted as substrates. The enzyme is shown to monohalogenate a diverse range of sterically and electronically different substrates. Fourteen substrates were selected (boxed), based on both interest in the product and their stability, for further verification through either scale up and spectroscopic characterisation of their product, or through comparison to synthetic standards that we generated and fully characterised. Iodinated products 1 and 2 were isolated from VirX1 biotransformations, whereas the regiochemistry for 3 - 14 was determined by comparison with synthetic standards, * denotes hypothesised halogenation site by VirX1 where the enzymatic product did not match with synthetic standards. Conversion levels, to the iodinated product, as estimated by LC-HRMS or UPLC analysis, are reported.