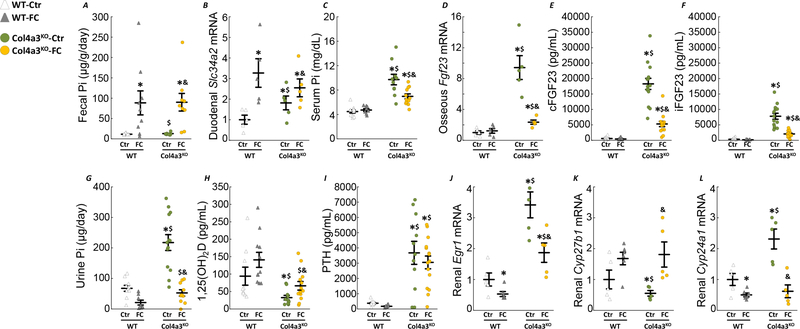
Figure 6: Ferric citrate administration in mice with early CKD decreases FGF23 production.
Levels of fecal phosphate (A), duodenal slc34a2 (B), serum phosphate (C), osseous Fgf23 mRNA expression (D), serum cFGF23 (E), serum iFGF23 (F), urine phosphate (G), serum 1,25(OH)2D (H) and serum PTH (I) in 10 week old WT and Col4a3KO mice fed a mineral sufficient diet (Ctr) supplemented or not with 5% ferric citrate (FC) during 6 weeks. Data are presented as mean ± SE, n≥8 per group, p<0.05 vs.* WT-Ctr, $ WT-FC, & Col4a3KO-Ctr mice. Renal mRNA expression of FGF23 targets, Egr1 (J), Cyp27b1 (K), Cyp24a1 (L). Data are presented as mean ± SE, n≥5 per group, p<0.05 vs.* WT-Ctr, $ WT-FC, & Col4a3KO-Ctr mice. Measurements performed in 10 week old WT and Col4a3KO mice fed a mineral sufficient diet (Ctr) supplemented or not with 5% ferric citrate (FC) during 6 weeks.