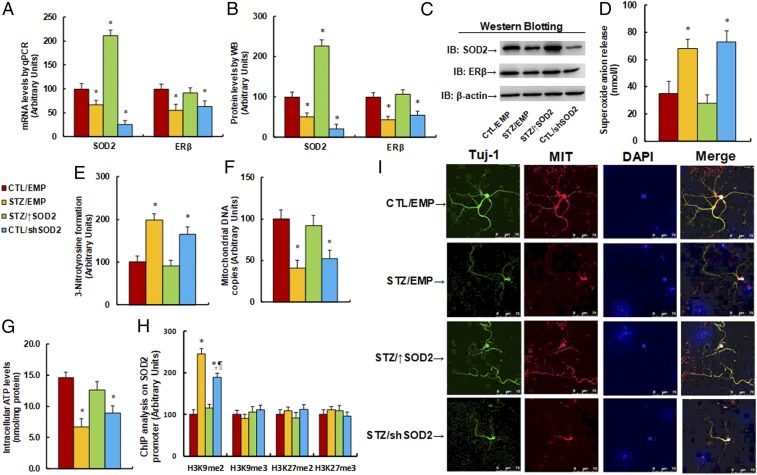
Fig. 4.
Maternal diabetes induces suppression of SOD2 and ERβ with oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, while SOD2 overexpression restores, and SOD2 knockdown mimics, this effect. The 6-wk-old male offspring from dams where diabetes (STZ) had been induced or from controls (CTL) received empty (EMP), SOD2 overexpression (↑SOD2), or SOD2 knockdown (shERβ) lentivirus infusion; then, the offspring at 8 wk of age were sacrificed for further analysis. (A–J) The amygdala tissues were isolated for further analysis as below: (A) mRNA levels for gene expression of SOD2 and ER (n = 4), (B) representative pictures for Western blotting, (C) quantitation of protein levels (n = 5), (D) in vivo superoxide anion release (n = 5), (E) quantitation of 3-nitrotyrosine formation (n = 5), (F) mitochondrial DNA copies (n = 4), and (G) intracellular ATP levels (n = 5). (H and I) The amygdala neurons were isolated at embryonic day (E18) from the above treatment for further analysis. (H) ChIP analysis for histone modification in amygdala neurons (n = 4). (I) Immunostaining in amygdala neurons. The Tuj-1 was stained as neuron marker (green), mitochondria (MIT) was stained by MitoBeacon (red), nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue), and “merge” means the mixed color of triple staining (*P < 0.05 vs. CTL/EMP group; ¶P < 0.05 vs. STZ/EMP group). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. (Magnification, 400×.)