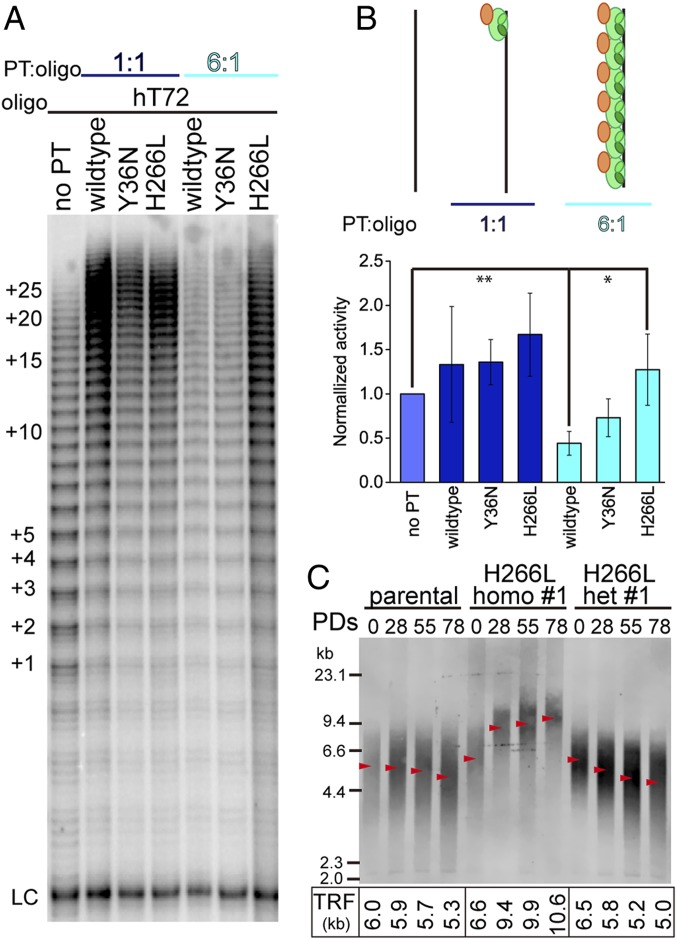
Fig. 3.
H266L POT1 mutant abrogates POT1-TPP1 complex-mediated inhibition of telomerase in a substrate length-dependent manner promoting telomere extension. (A) Direct in vitro telomerase assay performed on hT72 ssDNA. Lane 1, no POT1-TPP1 added. Lanes 2 to 4, stoichiometric concentration of POT1-TPP1 wild type, Y36N, and H266L were added, respectively. Lanes 5 to 7, POT1-TPP1 wild type, Y36N, and H266L were added to saturate all binding sites on hT72. LC, loading control. The number of telomere repeats being added is indicated at left. (B) Quantification of lanes in A displaying normalized telomerase activity. Schematic models indicate different binding states of POT1-TPP1 complexes bound to hT72. Error bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). **P < 0.005; 0.005 < *P < 0.05. (C) TRF analysis of genomic DNA from parental and CRISPR-Cas9 edited HCT 116 cell lines containing either homozygous H266L (homo #1) or heterozygous H266L (het #1) mutations at the indicated population doublings (PDs) in culture. Quantification of TRF length is indicated by red arrows with corresponding values shown below the gel.